This article describes the different cloud deployment models, explains how to choose the best model for your business based on your needs, and explores the pros and cons of each model.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing provides access to a shared pool of computer resources (servers, storage, programs, etc.) in the cloud. When you need additional resources, simply request them. Thanks to the cloud, it’s easy to get your resources up and running quickly. You can free up resources that are no longer needed. This method allows you to pay only for what you use. The cloud provider takes care of all the maintenance.
More details about cloud computing:
What are cloud deployment models?
Cloud deployment models act as virtual computing environments with different deployment architectures depending on the amount of data you store and the infrastructure you have access to.
Cloud deployment models identify specific types of cloud environments based on ownership, size, access, and the nature and purpose of the cloud. There are different deployment models, depending on the location and who manages the infrastructure.
Transforming Technology 2024: Explore the Evolution of Cloud Computing Architecture
For organizations considering adopting cloud services, the first step is to understand the deployment models available. Understanding these will help you make better decisions about which path your business should take. Each model has strengths and weaknesses in areas such as governance, scalability, security, flexibility, cost, and management.
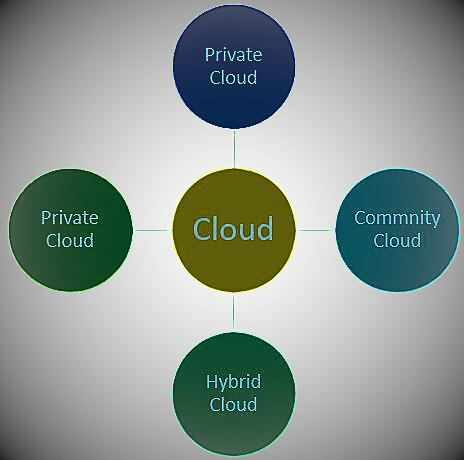
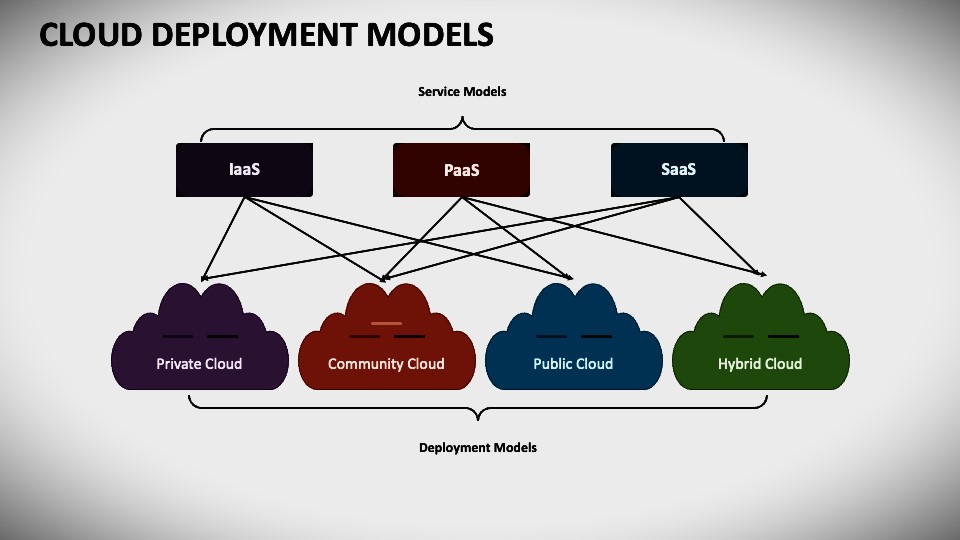
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models identify specific types of cloud environments based on ownership, size, access, and the nature and purpose of the cloud. Your cloud deployment model defines the location of your servers and who manages them. It specifies what your cloud infrastructure looks like, what you can change, what services are provided, or whether you have to build everything yourself. The relationship between infrastructure and users is also defined by the type of cloud deployment.
The different types of cloud deployment models are discussed below.
- Private cloud: resources managed and used by an organization.
- Public Cloud: Resources available to the general public on a pay-as-you-go model.
- Community cloud: resources shared by multiple organizations, usually within the same industry.
- Hybrid Cloud: This cloud deployment model is partially managed by the provided service and partially managed by the organization.
Cloud deployment models: Issues
Here are some common issues encountered during deployment:
- It is impossible to provide 100% availability without a high-availability architecture.
- Vendor lock-in is also always a concern for users, but it actually co-exists with vendor lock-in.
- It is almost impossible to guarantee 100% security and privacy protection.
- Corporate users need to manage their business legal documents.
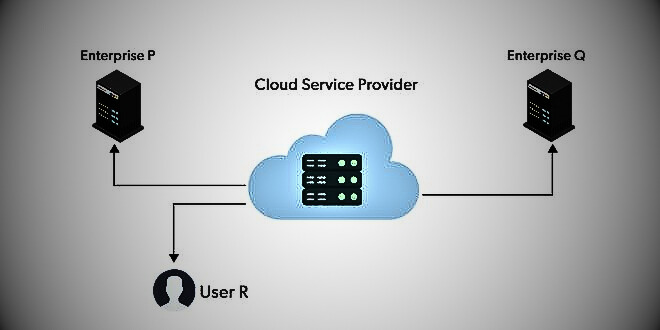
Public Cloud
Public clouds make systems and services accessible to everyone. Public clouds are available to everyone and may be less secure. A public cloud is a cloud that provides cloud infrastructure services to the general public and major industry organizations through the Internet. In this cloud deployment models, the infrastructure is owned by the entity providing the cloud service rather than the consumer. It is a type of cloud hosting that allows customers and users to access systems and services easily. This form of cloud computing is a great example of cloud hosting, where a service provider provides services to a variety of customers. Under this arrangement, storage backup and recovery services are provided either as a subscription or for free on a per-user basis. For example, Google App Engine.
Characteristics of Public Cloud
Important features of public clouds are:
- Uniformly designed infrastructure
- It works on pay-as-you-go basis
- Economies of scale
- SLA ensures that all users get a fair share of priority.
- High probability of data leakage due to multi-tenant architecture
Benefits of the public cloud model
- Minimal investment: As a pay-as-you-go service, it is ideal for businesses that need immediate access to resources without large upfront fees.
- No setup costs: There is no need to install any hardware as the entire infrastructure is fully subsidized by the cloud service provider.
- No infrastructure management required: When using a public cloud, no infrastructure management is required.
- No maintenance: Maintenance activities are performed by the service provider (not by the user).
- Dynamic scalability: access to on-demand resources to meet the needs of your enterprise.
Disadvantages of the public cloud model
- Less secure: Public clouds are less secure because their resources are exposed and do not guarantee a high level of security.
- Less customizable: Since it is accessed by many common users, it cannot be customized according to individual needs.
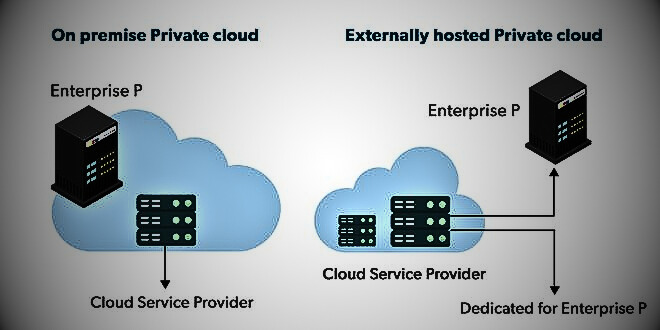
Private Cloud
The private cloud deployment model is the exact opposite of the public cloud deployment model. It is a one-on-one environment for one user (customer). There is no need to share your hardware with others. The difference between private cloud and public cloud is how all the hardware is managed. This is also known as “internal cloud” and refers to the ability to access systems and services within a specific perimeter or organization. Cloud platforms are implemented in a secure, cloud-based environment protected by strong firewalls and overseen by your organization’s IT department. Private clouds give you more flexibility in controlling your cloud resources.
Characteristics of Private Cloud
Important features of private cloud are:
- Infrastructure design is not uniform.
- The risk of data leakage is very low.
- Provides end-to-end control.
- Weak SLA, but custom policies can be enforced.
- Internal infrastructure to manage resources easily.
Benefits of Private Cloud Model
- Better control: You are the sole owner of the property. Get full control over service integration, IT operations, policies and user behavior.
- Data security and privacy: suitable for storing corporate information that is only accessible to authorized employees. Dividing resources within the same infrastructure can improve access and security.
- Support for legacy systems: This approach is designed to work with legacy systems that do not have access to the public cloud.
- Customization: Unlike public cloud deployments, private clouds allow businesses to customize the solution to suit their specific needs.
Disadvantages of private cloud model
- Less scalable: Private clouds scale within a certain limit due to the small number of customers.
- Higher cost: Private clouds offer more personalized features, which means higher costs.
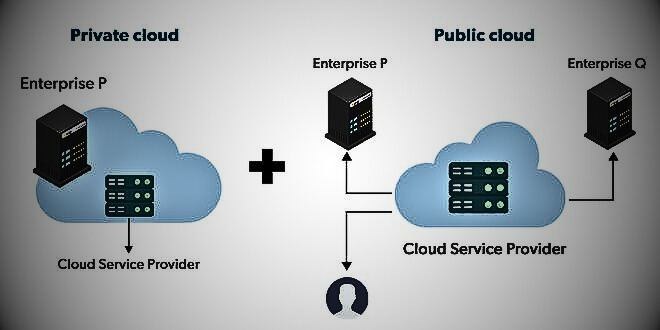
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud computing provides the best of both worlds by combining the public and private worlds with a unique layer of software. With a hybrid solution, you can host your apps in a secure environment while taking advantage of the cost savings of the public cloud. Organizations can combine two or more cloud deployment methods to move data and applications between different clouds, depending on their needs.
Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud
Hybrid cloud features include:
- Provides better security and privacy
- Better scalability
- Cost-effective cloud deployment models
- Simplify data and application portability.
Benefits of hybrid cloud model
- Flexibility and control: Flexible companies can design personalized solutions to meet specific needs.
- Cost: Public clouds provide scalability, so you pay for additional capacity only when you need it.
- Security: Since the data is properly segregated, the chances of data theft by an attacker are greatly reduced.
Disadvantages of hybrid cloud model
- Difficult to manage: Hybrid clouds are difficult to manage because they are a combination of both public and private clouds. So it’s complicated.
- Slow data transmission: In a hybrid cloud, data transmission is through the public cloud, which causes delays.
Top 10 best examples of Hybrid cloud computing
Community Cloud
It allows groups in your organization to access systems and services. It is a distributed system created by integrating services from different clouds to meet the specific needs of a community, industry, or business. Community infrastructure can be shared between organizations with common concerns and tasks. Usually managed by a third party or a combination of one or more organizations within the community,.
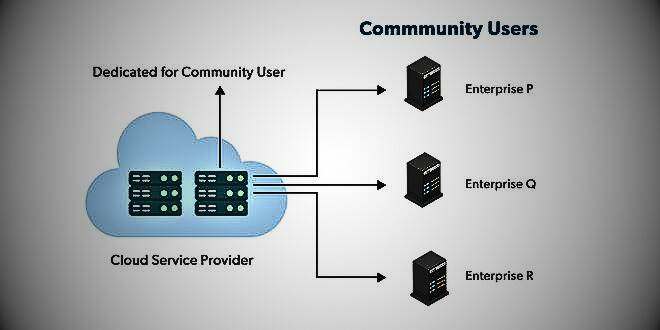
Benefits of Community Cloud Model
- Cost-effective: The cloud is shared by multiple organizations or communities, making it cost-effective.
- Security: Community clouds provide better security.
- Shared resources: Resources, infrastructure, etc. can be shared with multiple organizations.
- Collaboration and data sharing: suitable for both collaboration and data sharing.
Disadvantages of community cloud model
- Limited scalability: Community clouds have relatively low scalability because multiple organizations share the same resources based on their collective interests.
- Strict customization: Data and resources are shared among different organizations according to mutual benefit, so even if an organization wants to change it according to its needs, it cannot be changed because it will affect other organizations.
Multi-Cloud
As the name suggests, we are talking about the simultaneous adoption of multiple cloud providers under this paradigm. This is similar to the hybrid cloud deployment approach, which combines public and private cloud resources. Multicloud uses multiple public clouds instead of integrating private and public clouds. Although public cloud providers offer many tools to improve the reliability of their services, incidents still occur. It is very rare for an accident to occur due to two different clouds at the same time. As a result, multi-cloud deployment further improves the availability of your services.
Benefits of multi-cloud model
- By choosing different cloud providers, you can combine the best features of each cloud provider’s services to suit your apps, workloads, and business demands.
- Reduce latency: You can choose cloud regions and areas that are closer to your customers to reduce latency and improve the user experience.
- High availability of services: It is extremely rare for incidents to occur in two different clouds at the same time. Therefore, multi-cloud deployment improves the availability of services.
Disadvantages of multicloud model
- Complexity: The combination of multiple clouds complicates the system and can cause bottlenecks.
- Security issues: Due to its complex structure, it may contain vulnerabilities that hackers can take advantage of, making your data less secure.
Overall Analysis of Cloud Deployment Models
The overall Analysis of these models with respect to different factors is described below.
| Factors | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Community Cloud | Hybrid Cloud |
| Initial Setup | Easy | Complex, requires a professional team to setup | Complex, requires a professional team to setup | Complex, requires a professional team to setup |
| Scalability and Flexibility | High | High | Fixed | High |
| Cost-Comparison | Cost-Effective | Costly | Distributed cost among members | Between public and private cloud |
| Reliability | Low | Low | High | High |
| Data Security | Low | High | High | High |
| Data Privacy | Low | High | High | High |
Models of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing helps in rendering several services according to roles, companies, etc. Cloud computing models are explained below.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) helps provide computer infrastructure on an external basis to support operations. In general, IaaS provides services to network equipment, devices, databases, and web servers.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) helps large organizations and enterprises manage and build their own IT platforms. This infrastructure is flexible depending on the customer’s needs.
Top 8 Examples of IAAS in cloud computing: What You Need To Know In 2024
Benefits of IaaS
- IaaS is cost-effective, as it does not require any capital investment.
- IaaS cloud providers provide better security than other software.
- IaaS provides remote access.
Disadvantages of IaaS
- IaaS requires users to protect their data and applications.
- Cloud computing is not accessible in some parts of the world.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a type of cloud computing that provides a platform for developers to create applications and services over the Internet.
PaaS helps you maintain control over your business applications.
Benefits of PaaS
- PaaS is simple and accessible through a web browser, making it very convenient for users.
- PaaS has the ability to manage the lifecycle efficiently.
Disadvantages of PaaS
- PaaS offers less control over the environment and lacks some customization, giving you limited control over your infrastructure.
- PaaS is more dependent on the provider.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a service (SaaS) is a type of cloud computing model that delivers services and applications over the Internet. SaaS applications are called web-based or hosted software.
Almost 60% of SaaS is cloud solutions and hence it is mainly preferred by enterprises.
11 Best Popular Examples Of SaaS in Cloud Computing
Benefits of SaaS
- SaaS allows access to app data from anywhere on the Internet.
- Provides easy access to SaaS features and services.
Disadvantages of SaaS
- The customization of SaaS solutions is limited. That said, there are some limitations within the platform.
- SaaS gives you little control over your data.
- SaaS is usually cloud-based and requires a stable Internet connection to function properly.
Summary
- Cloud deployment is the installation of hardware and software that can be accessed over the Internet on a dedicated platform.
- The four most important cloud deployment models are: 1) public cloud, 2) private cloud, 3) community cloud, and 4) hybrid cloud.
- Public clouds are available to the general public, and resources are shared among all users.
- A private cloud deployment model is an environment dedicated to a single user (customer).
- A community cloud is a cloud-based infrastructure model that allows multiple organizations to share resources and services based on standard regulatory requirements.
- A hybrid cloud deployment model is a combination of public and private clouds.
- Organizations using a multi-cloud model incorporate public cloud services from multiple cloud service providers.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram

4 thoughts on “What is cloud deployment models? Definition, types, comparisons and examples”
Comments are closed.