This growing digital threat is rapidly gaining notoriety due to its sophisticated tactics and unique operational approach. Akira ransomware stands out with its unique payment options and dual extortion techniques. As Akira continues to evolve, monitoring and understanding its tactics is crucial for cybersecurity efforts.
First discovered in early 2023, Akira ransomware appears to be another ransomware family entering the market. Its continuous activity and large number of victims are the main motivations for investigating the inner workings of the malware and enabling the Blue Team to create additional defense rules in addition to the existing ones.
What is malware? History, Definition, 7 main types and real-world examples
The emergence of a dangerous internet ransomware virus called ‘Akira’ has raised concerns among cybersecurity experts and prompted warnings from the government.
This malicious software targets Windows- and Linux-based systems, encrypts sensitive personal data, and extorts money from victims.
This comprehensive article explains the techniques of the Akira ransomware group, how attacks occur, and what to do if Akira compromises your systems or machines. Also, learn how to protect your company’s sensitive and important data by taking simple precautions.
What is an Akira ransomware attack?
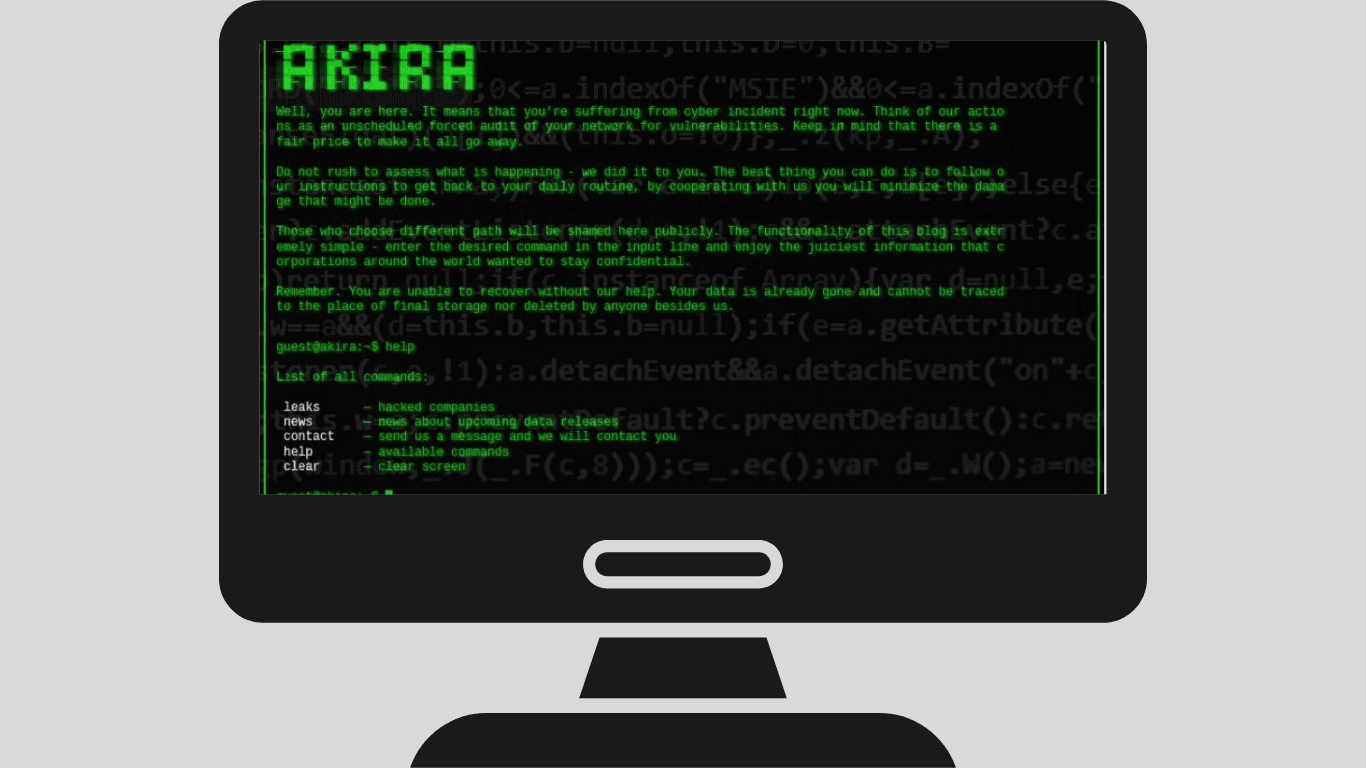
Ransomware is a type of malware that holds user data hostage and denies access until a ransom is paid.
Akira is a new ransomware family that first emerged in the United States and Canada in March of this year. Unlike other ransomware threats, Akira uses dual extortion techniques to steal and encrypt data, increasing the likelihood of extracting money from victims. This ransomware has already affected a large number of organizations, with 80% of victims being small and medium-sized businesses.
Akira ransomware is designed to encrypt data, create ransomware notes, and delete Windows Shadow Volume Copies on affected devices. Modify the file names of all encrypted files by adding the “.akira” extension. This ransomware is designed to shut down processes or shut down Windows services that may interfere with the encryption process. VPN services are used to trick users into downloading malicious files, especially if the user does not have two-factor authentication enabled.
What is the working mechanism of Akira ransomware?
Akira ransomware can enter your computer through various means, including malicious email attachments or links, pirated software websites, peer-to-peer (P2P) networks, free file hosting sites, and third-party downloaders.

Cybercriminals also use fake software updates and Trojan horses to deliver malware to unsuspecting users. When a user unknowingly downloads and executes a malicious file, Akira encrypts files located in various hard drive folders.
Certain system folders ending in .exe, .dll, .msi, .lnk, and .sys and folders located in the Windows, System Volume Information, Recycle Bin, and Program Data folders do not appear to be encrypted.
Once the files are encrypted, the malware can spread to other devices. The malware attempts to obtain Windows domain administrator credentials, which allows it to deploy ransomware across the network.
How to know if Akira ransomware has infected your system
If you are unable to open all your files, have strange file extensions, or see a note asking for money to get your files back, you may be infected with Akira ransomware.
In June 2023, Avast released a free decryption tool for Akira ransomware.
Although this decryption tool was successful in some cases, it has become ineffective in recent cases, leading us to believe that the vulnerability used has been fixed by the Akira ransomware group.
What are the signs of an Akira ransomware attack?
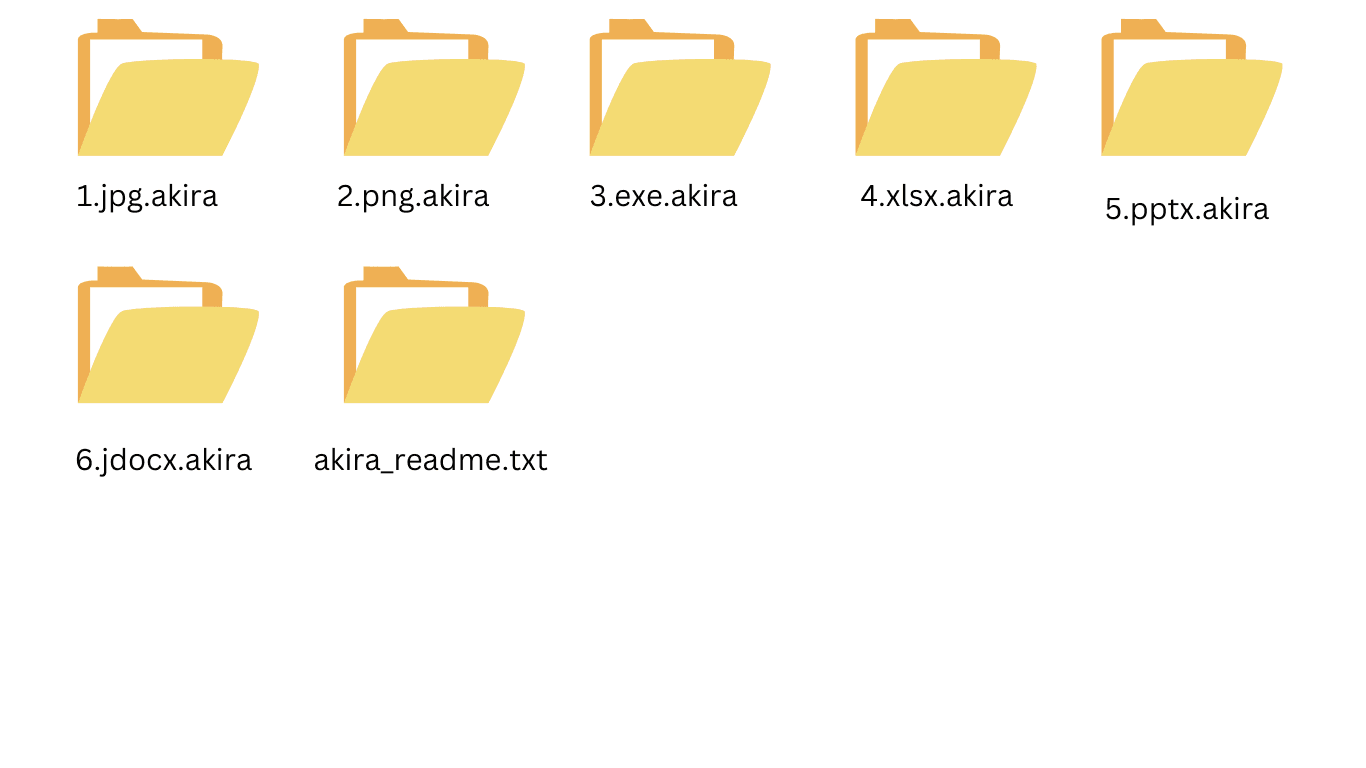

- The Akira ransomware places a text file named “akira_readme.txt” or another name (listed in the table below) in each encrypted folder.
- The file name will be changed to .akira or one of the other extensions listed in the table below.
- CPU usage is approaching 100%, even though I am not using the application.
- My PC seems to be running slower than normal.
- My hard disk is reading and writing at 100% capacity in the background, even though I am not using any applications.
- Antivirus software is not running or is disabled.
What to do if your data is encrypted by Akira
- If you suspect an Akira ransomware attack, immediately disconnect the affected machine from the network and shut it down normally.
- It is usually best not to communicate directly with hackers. Hackers are good at taking advantage of people under pressure. Professional negotiators always achieve better results.
- Report the incident to the relevant authorities. Many countries have police departments dedicated to cybercrime.
How do I protect against Akira attacks?
CERT-In advises users to follow basic internet hygiene and security protocols to ensure protection against ransomware. This includes maintaining updated offline backups of critical data to ensure no data is lost in the event of an attack. Additionally, it advises regularly updating all operating systems and networks and patching outdated systems and networks.
Companies should also establish sender policies for domain-based message authentication, reporting, conformance, domain key-identified mail (DKIM), and organizational email validation. This helps prevent spam by detecting email spoofing and callback phishing attacks. Strong password policies and multi-factor authentication (MFA) should be implemented. We also enforce strict policies to prevent the downloading of attachment types such as .exe, .pif, and .url from external devices to encrypt data during use, at rest, and in transit and protect it from malicious code. CERT also advises regular security audits of critical networks and systems, especially database servers.
Prevention against Ransomware Attacks
Futurism recommends the following precautions to keep Akira and various other nascent ransomware attacks at bay:.
- Regular backups: Maintain regular offline backups of all your important data. This allows you to restore your system to its previous state even if you fall victim to a ransomware attack.
- Software updates: Keep all software and systems up-to-date. Cybercriminals often exploit known vulnerabilities in software, so keeping your software updated with regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT) can help keep your system secure.
- Email attachments: Be wary of email attachments, especially those received from unknown senders. Many ransomware attacks are launched through malicious email attachments. Having a strong email security solution in place can go a long way toward avoiding such attacks.
- Firewall and antivirus: Use a reliable firewall and antivirus program. These can help detect and block ransomware.
- Avoid suspicious links: Don’t click on suspicious links, whether in emails, text messages, or online ads.
- Educate your employees: If you’re a business, educate your employees about the risks of ransomware and how to avoid falling victim to it.
- Use strong, unique passwords. Using strong, unique passwords makes it harder for ransomware to gain access to your systems.
- Enable multi-factor authentication: Whenever possible, enable multi-factor authentication using a strong identity and access management (IAM) solution. This adds an additional layer of security that can prevent ransomware attacks.
Implement zero-trust security: Many cybersecurity strategies are inadequate to combat threats emanating from the dark web. Additionally, these strategies often lack the necessary intelligent threat insights. Futurism recommends implementing a zero-trust security model to address these security issues. This framework enhances risk management by eliminating assumed trust. The Zero Trust security model prioritizes security regardless of the user’s location, context, identity, or access method/platform. It provides operational, strategic, and intelligent insights for security administrators and IT professionals, allowing them to filter out unnecessary noise and respond quickly to threats.
Summary of Akira Ransomware
| Name | Akira / Akira Ransomware |
| Danger Level | Very High. Military-grade encryption and frequent data exfiltration attacks. |
| Release date | 2023 |
| Affected Systems | Very high. Military-grade encryption and frequent data exfiltration attacks. |
| File Extensions | .akira |
| Ransom demands | “akira_readme.txt” |
| Contact method/email | Through a hidden TOR web service |
| Known scammers | None |
Interesting topics about cybersecurity. You must know
- 10 Common Computer Security Threats You Must Know About
- 5 types of Computer security: definitions, Importance, Threats, and best examples in 2024
- Unlocking Resilience: 8 Key Components of an Adaptive Network Security Model
- Unlocking Success: The Essential Keys to “Network Security Key” Excellence
- Mastering Network Security: 10 Vital Steps for Ultimate Protection
- 12 types of Phishing attacks: Prevention, causes, techniques and examples
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram

