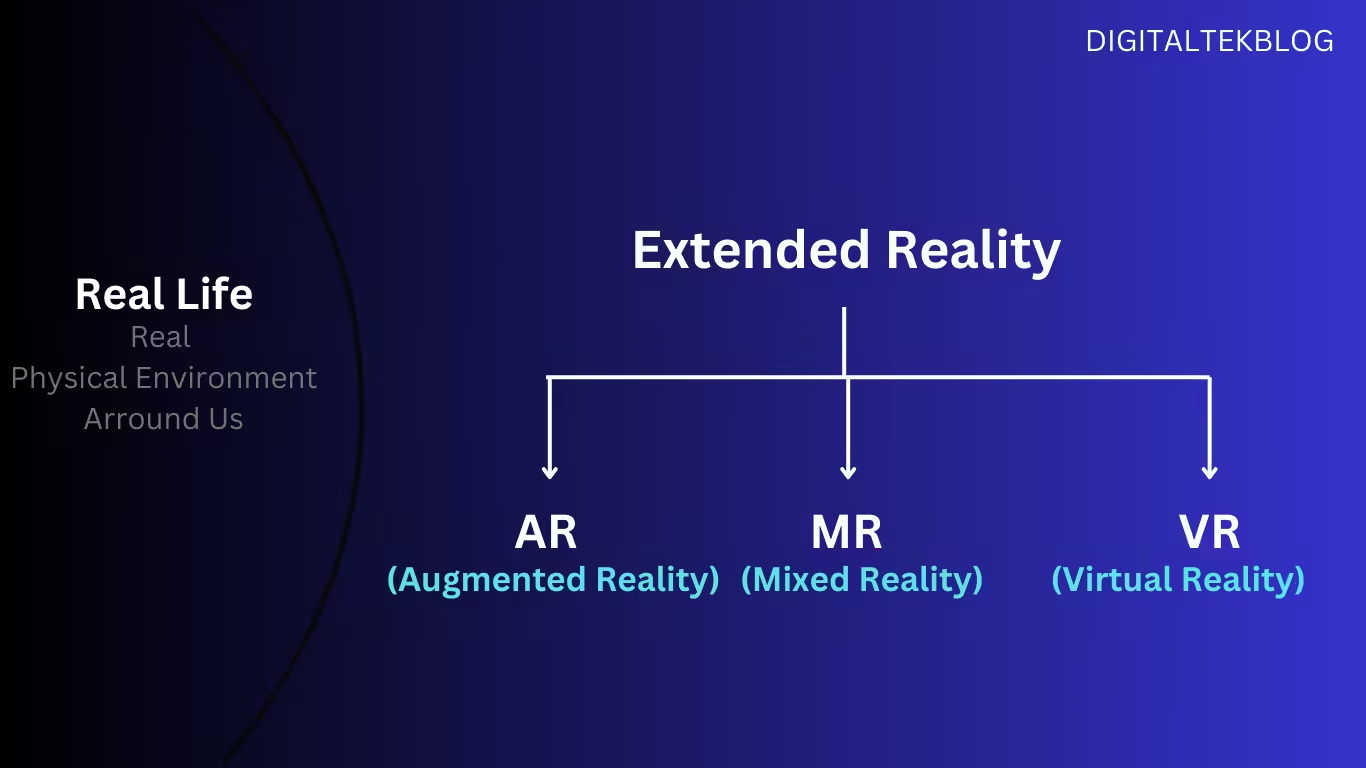
Extended reality (XR) encompasses virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and mixed reality (MR) technologies and represents the convergence of immersive technologies that blend the physical and virtual worlds. These cutting-edge innovations have the power to transform the way we interact with the digital realm, from games and entertainment to business and education applications.
In recent years, advances in augmented reality have created new opportunities across a variety of sectors, allowing users to create, collaborate, and explore in computer-generated environments like never before. XR continues to grow and has the potential to revolutionize industries, change the way people interact with the digital world, and improve productivity, communication, and the overall user experience.
What is Extended Reality (XR)?
Extended Reality (XR) is a broad term for any technology that alters reality by adding some degree of digital elements to the physical or real-world environment, including augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and virtual reality (VR). Including but not limited to.
New technologies that combine the physical and virtual worlds also fall under XR. The “X” in XR represents a variable (any letter of the alphabet) that may be used in such technologies in the future.
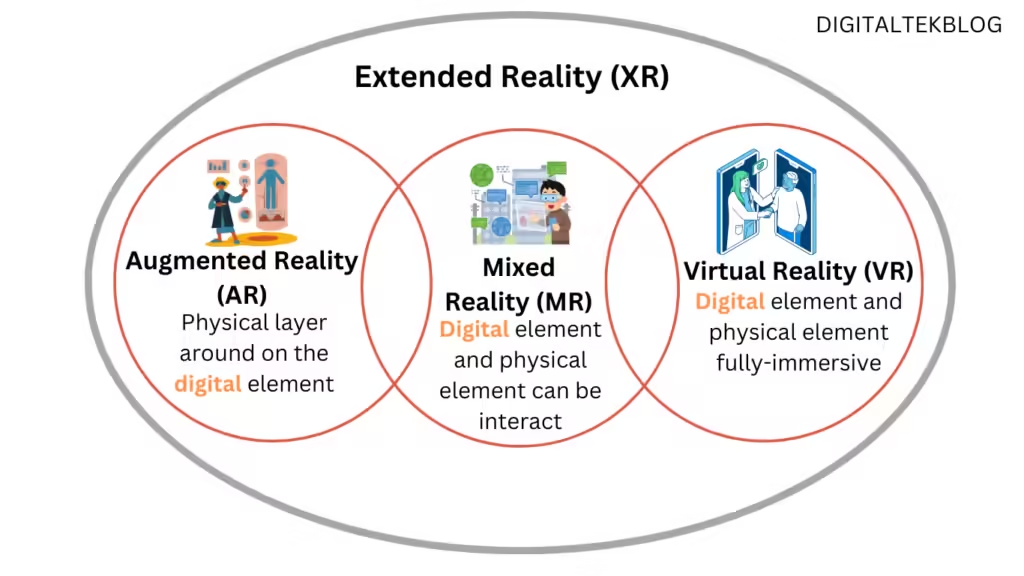
Extended Reality (XR) is a combination of Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and Virtual Reality (VR), and any type of technology is blended with the physical and digital world.
Therefore, the term augmented reality does not refer to a specific technology but rather to any technology to be created in the future that alters reality by merging the digital and physical worlds or by creating a completely virtual environment.
Extended reality (XR) is a broad term for technologies that enhance or replace our worldview. This is often achieved by overlaying or immersing computer text and graphics into the real world or virtual environments. Or perhaps a combination of both.
XR includes augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR). All three of these “realities” have similar features and requirements, but each has a different purpose and underlying technology.
XR should play a fundamental role in the metaverse. The “next evolution of the Internet” will integrate the real, digital, and virtual worlds into a new reality, accessed through arm-powered “gateway” devices such as VR headsets and AR smart glasses.
XR technologies have some basic similarities. At the core of all XR wearable devices is the ability to navigate the world and display relevant information using visual input methods such as objects, gestures, and eye tracking. Depth perception and mapping are also enabled by depth and positioning capabilities. However, XR devices differ in the type of AR, MR, and VR experiences and the complexity of the use case they are designed to achieve.
Components of Extended Reality
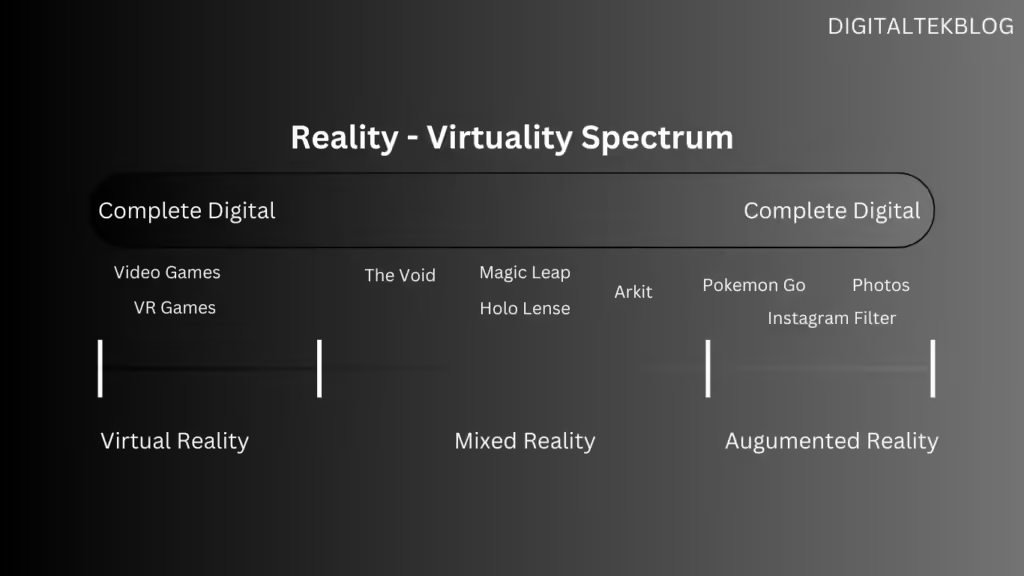
Extended Reality (XR) is an immersive learning technology that is included with augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (MR).
What is augmented reality (AR)?
Augmented reality (AR) is a technology that applies digital information to a user’s real-world environment to enhance their perception of reality. This can be achieved using devices such as smartphones, tablets, and special AR glasses. Users can experience AR through a variety of applications, including gaming, education, navigation, and more. This technology combines the physical world with virtual elements to provide users with an augmented experience without cutting them off from their surroundings. Examples of AR applications include Pokémon Go and Snapchat filters.
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the way we see the real world by overlaying computer-generated information on what we see. Currently, this technology is widely used in smartphone AR applications that require the user to hold the smartphone in front of their eyes. By capturing images from the camera and processing them in real-time, apps can display relevant information and provide gaming and social experiences that appear rooted in the real world.
Although smartphone AR has improved significantly over the past decade, its applications remain limited. There is a growing focus on providing a more holistic AR experience through wearable smart glasses. These devices must combine ultra-low power processors and multiple sensors, such as depth perception and tracking, with a lightweight form factor that is comfortable to wear for long periods of time.

AR smart glasses require always-on, intuitive, and safe navigation when the user is on the move. This requires significant advancements in features such as depth, occlusion (when one object in 3D space blocks the view of another), semantics, location, orientation, position, posture, gesture, and eye tracking.
Several new smart glasses models hit the market in 2021, including Snap’s Spectacle Smart Glasses, Lenovo Think Reality A3, and Vuzix’s Next Gen Smart Glasses. As explained in the video below, AR smart glasses are set to improve the lives of all of us in the future. It can also serve as a gateway to the metaverse, where virtual elements and reality intersect.
What is Virtual reality (VR)?
Virtual reality (VR) is a technology that transports users away from the physical world and completely immerses them in a computer-generated environment. To experience VR, users typically wear a headset with a display that covers their field of view. Advanced VR systems also include hand controllers and tracking sensors for a more interactive and immersive experience. VR has applications in a variety of industries, including gaming, therapy, and training simulations. Popular VR devices include the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive.
Virtual reality (VR) completely changes the user’s perspective and immerses the user in a computer-generated virtual environment. This type of XR technology has existed for some time and has been gradually improved. It is mainly used for entertainment experiences such as games, concerts, movies, and sports, but it is also becoming increasingly popular in the social sector. For VR, immersive entertainment experiences require features such as HD rendering pipelines, volumetric capture, 6DoF motion tracking, and facial expression capture.
VR is also used as a training tool and in education and healthcare, including rehabilitation. To make these experiences possible (and seamless) for end users, VR technology often focuses on high-quality video and rendering and ultra-low latency.

Finally, VR devices are enhancing the video conferencing experience through platforms like Recroom, which enables virtual meetings in various virtual worlds. Recroom, which currently supports the Oculus Quest, was featured in the third episode of Arm’s New Reality series in 2020, discussing immersive experiences with VR.
Some VR devices need to be connected to a PC, but standalone VR devices, like the pictured Oculus Quest 2, can deliver AAA games and metaverse experiences. Powered by high-end Arm processors, these standalone VR devices can be taken anywhere. In the future, standalone VR devices will become gateway devices to the metaverse.
What is Mixed Reality (MR)?
Mixed reality (MR), also known as hybrid reality or mediated reality, combines AR and VR technologies. It combines aspects of both virtual and real-world environments, allowing users to interact with digital content and the physical world simultaneously. Mixed reality can be experienced on devices such as the Microsoft HoloLens and the Magic Leap One. MR technology is closely related to immersive experiences in industries such as gaming, education, and healthcare. MR allows users to manipulate virtual objects and collaborate with others in a space that blends the digital and the physical. Applications for MR include remote assistance, architectural design, and entertainment.
MR sits between AR and VR because it blends the real and virtual worlds. There are three main scenarios for this type of XR technology. The first is a scenario where a smartphone or AR wearable device is used to superimpose virtual objects and characters onto a real-world environment, or vice versa.

Pokémon Go, a mobile game that became a huge hit worldwide in 2016, uses a smartphone camera to superimpose virtual Pokémon onto a real-world environment (also demoed using the HoloLens 2 at Microsoft Ignite 2021). Although it is often promoted as a revolutionary AR game, it is actually a great example of MR, blending the real-world environment with computer-generated objects.
Mixed reality is also starting to be used to impose VR real-world players onto video games, bringing real-world celebrities to game streaming platforms like Twitch and YouTube.
Applications of Extended Reality
Gaming
Augmented reality (XR) is having a huge impact on the gaming industry, providing immersive and interactive experiences for players. Games like Pokémon Go combine augmented reality with real-world environments, and VR headset games like Beat Saber and Oculus Rift exclusives immerse players in virtual worlds. Head-mounted displays like the Oculus Quest 2 allow gamers to experience 3D environments, improving their gaming experience.
Health Care
The healthcare industry is beginning to adopt augmented reality technology, which is providing new opportunities for training and patient care. Medical professionals are using virtual reality to simulate surgery and other procedures for more effective training. Additionally, therapy employing VR and AR can help patients suffering from mental illnesses such as PTSD by exposing them to controlled, immersive environments.
Education
Educational institutions are starting to implement augmented reality to improve learning outcomes. Microsoft HoloLens allows students to interact with 3D models in a mixed reality environment. These immersive learning experiences help students gain a deeper understanding of complex topics and retain information more effectively.
Real Estate
The real estate industry is finding many uses for augmented reality. A virtual walkthrough of a property allows potential buyers to explore a home without being physically present. Additionally, real estate agents can use augmented reality tools to show clients how to renovate or customize a property, helping buyers visualize their future home.
Sports
In the world of sports, augmented reality technology is increasingly being used to improve training and performance. Virtual production technology allows athletes to practice in a simulated environment and receive real-time feedback and data analysis. Plus, immersive experiences like virtual stadiums give fans new ways to engage with their favorite teams.
Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry is increasingly adopting augmented reality to streamline processes and increase efficiency. Using VR and AR technology, engineers can visualize product designs and make necessary adjustments before production. Also, XR can be used to train factory workers, reducing the risk of accidents and promoting more efficient workflows.
The Future of Extended Reality
Extended Reality and 5G
The advent of 5G technology is expected to revolutionise augmented reality (XR) applications. With significantly faster data transfer speeds and lower latency than 4G, 5G enables seamless, real-time interactions in XR environments. This results in reduced motion sickness, improved quality of virtual reality and augmented reality content, and a better overall user experience.
Additionally, 5G’s ability to process large amounts of data allows for the integration of advanced XR elements such as real-time 3D rendering, artificial intelligence, and advanced simulations. These improvements will enable innovative XR applications in a variety of sectors, including healthcare, education, and entertainment.
Extended Reality and Digital Twins
Digital twins will play a key role in the future of extended reality 8, as they enable accurate simulation and monitoring of real-world scenarios in virtual environments. By combining the power of XR with digital twin technology, industries can create immersive and interactive 3D representations of physical assets, systems, and processes.
For example, manufacturing companies can use XR and digital twins to optimize production lines, troubleshoot equipment problems, and provide remote training to employees. In terms of urban planning, city developers can leverage XR to visualize and manipulate digital replicas of their infrastructure for better decision-making and increased efficiency.
In conclusion, the future of extended reality is closely linked to advancements in 5G and digital twin technology. By leveraging each feature, we can expect to see more interconnected, immersive, and realistic XR experiences across various sectors.
Extended Reality in Real World
Headsets
Augmented reality (XR) headsets are an essential part of immersive experiences as they allow users to explore virtual environments and interact with digital content. XR headsets come in a variety of types, from those designed for virtual reality (VR) to those designed for augmented reality (AR) or mixed reality (MR) experiences.
VR headsets such as the Oculus Rift and HTC Vive typically completely cover the user’s face, completely blocking out the real world around them. These headsets offer a 360-degree immersive experience and require sensors or cameras to track the user’s movements. In contrast, AR headsets such as Microsoft HoloLens overlay digital content on the user’s view of the real world, allowing users to interact with virtual objects and access information while remaining aware of their surroundings.
Smart Glasses
Smart glasses are another important piece of hardware in the augmented reality ecosystem. These devices look like regular glasses but are equipped with various sensors, cameras, and displays that allow users to access AR applications and information on the go. Some smart glasses, such as Google Glass, are primarily aimed at corporate use, while others, such as the Nreal Lite, are intended to provide consumers with an AR experience.
AR smart glasses typically have a more compact form factor than XR headsets, making them better suited for everyday use. These devices connect to the user’s phone or a dedicated processing unit that enables the AR experience. Unlike larger XR headsets, smart glasses typically have smaller displays and a limited field of view.
Augmented reality experiences rely heavily on the capabilities of headsets and smart glasses to provide users with immersive and interactive content that combines digital and real-world elements. As technology advances, we expect to see continued innovation in these key hardware components, further expanding the possibilities for XR applications.
10 processing steps of Digital Image Processing: A Learning Tutorial with best examples
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram