In this article, we will discuss the 7 major differences between edge computing and cloud computing. But before we discuss, let’s see an overview of edge computing and cloud computing. You can see more details about edge computing and cloud computing by clicking on the below link.
In the dynamic world of digital technology, cloud and edge computing have emerged as important paradigms that are reshaping the way enterprises manage data and applications. Although, at first glance, they may seem similar, these two technologies serve different purposes and offer unique benefits. SUSE, the world leader in open source software, including Linux products, is playing a key role in this technological shift, providing solutions for both cloud and edge computing needs. Understanding the difference between cloud computing and edge computing is important for businesses, especially those who want to leverage these technologies to improve operational efficiency.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing enables the deployment of computing resources and communication technologies through integrated computing infrastructure and transmission channels.
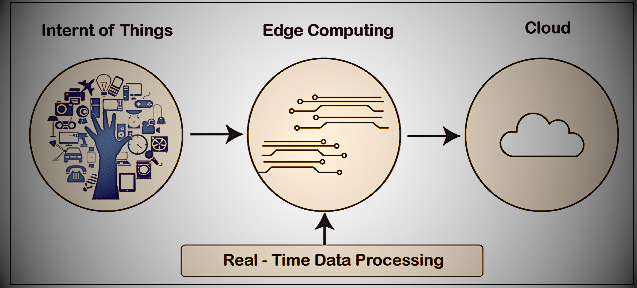
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that brings computing and data storage closer to the data source. Data processing occurs at the edge of the network, close to the devices generating the data, rather than in a central location such as a data center. The desired outcome of edge computing is to reduce latency and bandwidth needs when transferring large amounts of data across processing centers. Edge computing facilitates real-time decision-making by processing data near the edge and accelerating data transfer to and from the cloud.
IoT devices, self-driving cars, and augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) systems especially need the low-latency benefits of edge computing. Applications that generate large amounts of data, such as industry, video and image analysis and intelligent applications
Edge computing allows you to meet your computational needs more easily. Anywhere you need to collect information or perform a specific activity, you can do it in real time. The two main benefits typically associated with edge computing are increased efficiency and lower operating costs, which are defined below.
Advantages of Edge Computing
Some advantages of edge computing are discussed below:
1. Security
While the advent of IoT edge computing devices increases the overall attack vector for networks, it also provides some important security benefits. Because traditional cloud computing architectures are inherently centralized, they are highly vulnerable to distributed denial of service (DDoS) exploits and power failures.
Edge computing distributes compute, storage, and apps across different devices and cloud services, making it impossible to shut down a service due to a single failure.
2. Speed
The most important benefit of edge computing is its ability to improve network productivity by reducing latency. Because IoT edge computing devices are managed in private or near-edge data centers, stored data does not have to travel as far as in traditional cloud environments.
For many companies, speed is essential to their business model. For example, the financial industry depends on high-frequency trading algorithms, so a delay of just a few milliseconds can have a serious impact. In the medical industry, missing a few seconds can be a matter of life and death. And for companies that provide data-driven utilities to consumers, slow speeds can frustrate consumers and cause long-term damage to brands.
3. Performance Improvement
Edge computing not only collects data for transfer to the cloud but also collects, analyzes, and takes appropriate action on the collected data locally. These tasks can be accomplished in milliseconds, but optimizing technical information is critical to any operation.
Transmitting large amounts of data cost-effectively and in real time, especially from isolated industrial plants, can be a hurdle. This problem is solved by adding intelligence to tools available at the network edge. Edge computing brings analytical tools closer to the computer by removing the middleman. This configuration provides a low-cost option to maximize asset efficiency.
4. Reducing Operational Costs
In the cloud computing model, communications, data management, throughput and performance capabilities are astonishingly expensive. Edge computing, with very low bandwidth demands, eliminates this inefficiency. Edge computing implementation creates a useful continuum from computer to cloud that can accommodate the vast amounts of data collected. There is no need to transfer gigabytes of data to the cloud, eliminating the need for expensive bandwidth improvements.
Edge computing actually has the potential to reduce reliance on the cloud and, in response, increase the speed of data analysis. Additionally, there are some modern IoT devices with abundant processing power and storage. The move toward edge computing power will allow these devices to be used to their full potential.
5. Scalability
Companies can’t always anticipate their IT infrastructure needs as their business grows, and building a dedicated private cloud may be an unnecessary expense. There is also the issue of significant upfront construction costs and ongoing maintenance versus tomorrow’s requirements. Traditional private facilities impose artificial limits on growth and prevent companies from predicting future computing needs.
6. Reliability
It is no surprise that edge computing offers superior performance in relation to the security benefits it provides. IoT edge computing systems and cloud network infrastructure located directly at end users reduce the risk of network problems in remote locations impacting local customers. Even in the event of a local datacenter failure, IoT edge computing systems can continue to operate efficiently by performing critical processing tasks on their own wirelessly.
With many edge computing devices and edge network infrastructures connected to the network, it becomes even more difficult to completely shut down services. Information can be redirected through multiple channels to help customers maintain access to the resources and information they need. The result is unparalleled sustainability for the mass adoption of IoT edge computing devices and edge data centers into broader edge architectures.
7. Versatility
Edge computing interoperability makes edge computing extremely flexible. By working with local edge data centers, businesses can enter competitive markets faster without continuing to make expensive infrastructure investments. Edge data centers allow anyone to effectively serve end users with few physical barriers or delays. This is extremely valuable for content creators looking to provide unlimited subscription services.
Edge computing also enables IoT systems to collect significant amounts of contextual insights. Instead of waiting for a user to log into a device and communicate with a tiered data center, edge computing devices are always running, always connected, and always producing data for future evaluation.
Disadvantages of Edge Computing
1. Less processing power: Edge computing devices often have less processing power and storage capacity compared to cloud computing infrastructure. As a result, the types of apps available on Edge devices may be limited.
2. Increased complexity: Edge computing can be more difficult to implement than standard cloud computing strategies. This is due to edge computing’s need to locate processing and storage resources close to the source, which is difficult to manage and maintain.
3. Increased cost: Edge computing can be more expensive than cloud computing in terms of hardware and maintenance costs. This is because edge computing requires processing and storage resources to be deployed across multiple platforms, which can be expensive to set up and maintain.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is defined as the use of various resources, such as application development frameworks, storage, servers, and other software, through Internet access.
Cloud service providers have three common characteristics described below.
- The Service is flexible
- The cost of the equipment used (which may include memory, preparation time, bandwidth, etc.) must be borne by the user.
- The backend of the software is controlled by the cloud service provider.
Cloud computing Service Models
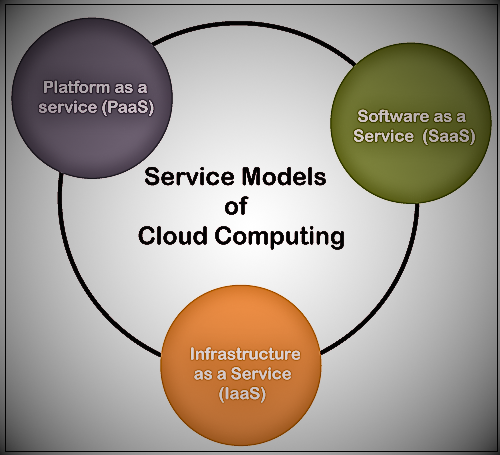
Regarding the market structure, cloud computing systems can be implemented, which may vary depending on the specific needs. Some of the traditional application services in use are briefly listed below. they are-
1. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS allows consumers to browse platforms and access software and cloud implementations. The operating system and Internet connection are not controlled by the user, which may limit the scope of software that can be implemented. Examples include Amazon Web Services, Rackspace, and Microsoft Azure.
2. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS requires customers to purchase the right to access or use a program or service hosted in the cloud.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS allows customers to monitor and manage operating systems, software, network access, and storage without having to manage the cloud.
Cloud computing Deployment Models
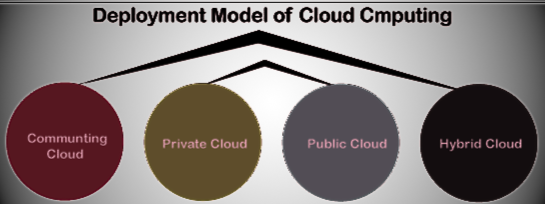
Cloud computing virtualization technologies depend on the prerequisites as well as the deployment model. There are four main types of models, each with unique features.
1. Community Cloud
Cloud-based infrastructure and services make the cloud accessible to many companies with similar goals and needs. As a result, it is disseminated by various organizations that use it. This reduces capital expenditure. These activities may be conducted on-site with the assistance of third parties.
2. Private Cloud
Private clouds are deployed, managed, and controlled only for specific organizations.
3. Public Cloud
Public clouds are used by citizens on a subscription basis but are operated by cloud service companies. Therefore, customers can build and implement services without the significant financial resources required for other deployment options.
4. Hybrid Cloud
Many types of clouds include these types of cloud services. However, such clouds have the ability to move data and apps from one domain to another. A hybrid cloud can also be a combination of public and private clouds.
Advantages of Cloud computing
Amidst the many challenges posed by cloud computing, some of the benefits of cloud computing are defined below.
1. Flexibility
Cloud computing allows businesses to operate with smaller cloud implementations and grow much more quickly and effectively. Depending on the situation, you can quickly downsize. Companies can also add additional resources to meet growing consumer demand if needed.
2. Consistency
System protection and recovery processes are supported by service providers using various disabled web pages.
3. Save money
By increasing their computing capabilities, businesses can significantly reduce their capital and operating expenses through cloud computing.
4. Mobile access
Mobile connectivity is also significantly supported by cloud computing.
5. Maintenance
Cloud computing providers often perform maintenance tasks.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
1. Security Risks: Cloud computing can raise additional security concerns, especially when security precautions by cloud providers are modest. This includes data breaches, unauthorized access and other cyber attacks.
2. Depend on Internet connectivity: Cloud computing requires an Internet connection to access computing resources and data. If your internet connection is unstable or slow, then it can be a disadvantage, as it can lead to reduced productivity and service.
3. Limited Control: As a result of cloud computing, the amount of control that businesses can have over their computing resources and data may be limited. Since businesses rely on cloud service providers to manage and maintain their computer infrastructure, they may not be able to fully personalize and optimize their systems.
Differences between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing
| Parameter | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
| Definition | Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that integrates computing and data. Storage close to the data source. | Cloud computing is a model of providing information technology services over the Internet. |
| Location of Processing | Processing occurs at the edge of the network, near the devices generating the data. | Data analysis and processing occur in a central location, such as a data center. |
| Bandwidth Requirements | Data is processed closer to the source, so less bandwidth is required. | It requires higher bandwidth than edge computing because data has to be sent to a central location over the network for processing. |
| Costs | Edge computing is more expensive because it may require specialized hardware and software at the edge. | Cloud computing is inexpensive because users pay only for the resources they actually use. |
| Scalability | Scalability of edge computing can be more difficult because additional computing resources may need to be added at the edge. | It is easy for users to quickly and easily increase or decrease their computing resources based on their needs. |
| Use Cases | Applications that require low latency and real-time decision-making, such as IoT devices, self-driving cars, and AR/VR systems,. | Applications that do not have strict latency requirements, such as web applications, email, and file storage,. |
| Data Security | Data is processed close to the source and not sent over the network, improving data security. | Data security becomes even more difficult as data is sent to a central location over the network for processing. |
Conclusion
Edge computing is becoming an emerging approach with the development of IoT because of the difficult and complex challenge of handling millions of sensors and devices and the associated resources required by them. This moves data computing and storage to the “edge” of the network, closer to end users, reducing traffic flow and reducing IoT bandwidth requirements compared to cloud computing models. Edge computing also reduces communication latency between edge/cloudlet servers and end users, resulting in faster response times than traditional cloud services for real-time IoT applications.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram

2 thoughts on “7 Big differences between edge computing and cloud computing: Advantages and disadvantages”
Comments are closed.