Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is also known as Hardware as a Service (HaaS). It is one of the layers of a cloud computing platform. It allows customers to outsource IT infrastructure such as servers, networking, processing, storage, virtual machines, and other resources. Customers access these resources over the Internet using a pay-as-you-go model.
Cloud computing refers to the availability of the hardware, software, and other technologies needed to create applications on demand over a network. Cloud computing providers offer a variety of models to facilitate cloud customers.
IaaS is the most basic layer of the cloud computing service model. The other two basic layers are PaaS (Platform as a Service) and SaaS (Software as a Service). The IaaS layer includes the hardware required to host applications, such as network, compute, and storage resources.
In traditional hosting services, IT infrastructure is rented for a specific period with a predetermined hardware configuration. The customer paid for the configuration and time, regardless of actual usage. With the help of the Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud computing platform layer, customers can dynamically scale the configuration to meet changing requirements and are billed only for the services actually used.
The IaaS cloud computing platform layer eliminates the need for any organization to maintain its IT infrastructure.
13 major differences between IAAS PAAS and SAAS: Here you know
What is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing?
All the physical resources or hardware, like laptops, desktops, cables, switches, routers, data centers, storage devices, etc, are part of the infrastructure. In cloud computing, all infrastructure is virtualized and provided as a service to consumers. It is called Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
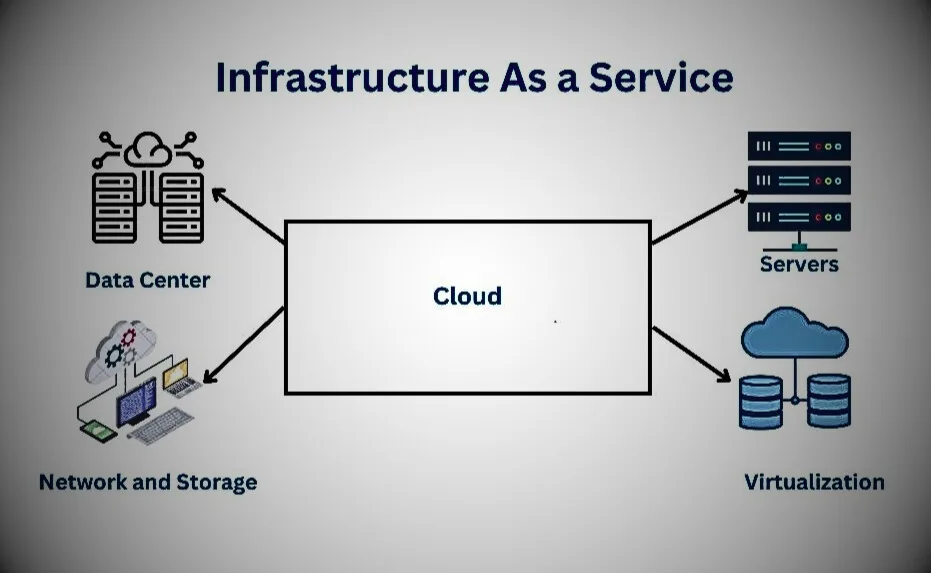
IaaS provides organizations with better control and management of applications without maintaining infrastructure (physical resources).
IaaS is offered in three models: public cloud, private cloud, and hybrid cloud. A private cloud means that the infrastructure resides on the customer’s premises. While a public cloud is located in the cloud computing platform vendor’s data center, a hybrid cloud combines the best of both public and private clouds chosen by the customer.
Characteristics of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Scalability: IaaS allows users to adjust computing power on demand without requiring long lead times or upfront hardware purchases.
- Virtualization: IaaS uses virtualization technology to abstract physical computer resources into virtualized instances that can be managed and distributed on demand.
- Resource pooling: This feature allows users to share computer resources such as network and storage among a large number of users, maximizing resource utilization and reducing costs.
- Elasticity: IaaS allows users to dynamically change computing resources as demand changes, ensuring optimal performance and financial feasibility.
- Self-service: IaaS provides a “self-service” portal that allows consumers to independently deploy, manage, and monitor computing resources without the assistance of IT staff.
- Availability: To ensure the high availability and reliability of their services, IaaS providers often operate redundant, geographically dispersed data centers.
- Security: To protect their infrastructure and customer data, IaaS companies adopt security measures such as data encryption, firewalls, access controls, and threat detection.
- Customization: IaaS allows users to modify the operating system, application stack, and security settings of the virtualized instance to suit their needs.
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides virtualized computing resources to users on a payment basis.
Users can scale resources up or down as per demand, taking advantage of high availability, security and optimization possibilities.
Services of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
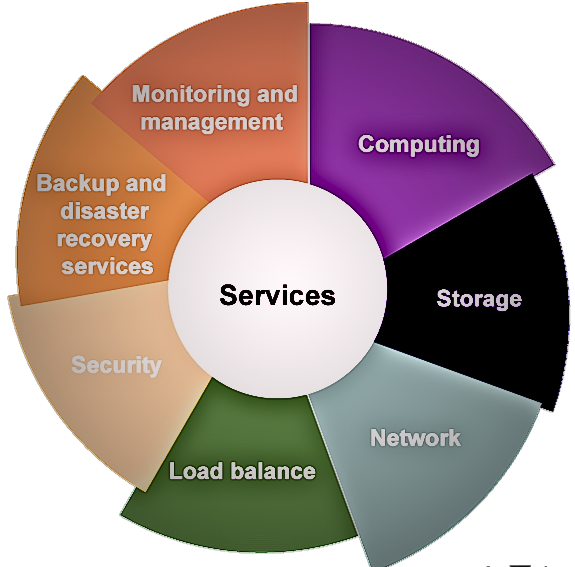
- Computing: To provision virtual machines (VMs) to end users, IaaS providers provide virtual central processing units (CPUs) and virtual main memory. As a result, users can run workloads and apps on the provider’s infrastructure without worrying about managing the underlying hardware.
- Storage: Backend storage services are provided by IaaS providers and allow users to store and access files and data. It provides a scalable and reliable storage solution for a variety of use cases and can include block storage, object storage, or file storage options.
- Networking: IaaS providers provide networking equipment such as routers, switches, and bridges for VMs through Network as a Service (NaaS). It enables connectivity and communication between VMs and other resources while allowing customers to create and maintain network architectures in their IaaS environments.
- Load Balancer: Infrastructure layer load balancing services are provided by IaaS providers. A load balancer divides incoming network traffic across multiple virtual machines (VMs) or resources, resulting in effective resource management and high availability of applications and services.
- Security: Security features and services are often provided by IaaS providers as part of their services. This includes network security, firewall configuration, access controls, encryption, and other security measures to protect the data and resources stored on your IaaS platform.
- Backup and disaster recovery services are provided by some IaaS providers and allow customers to create backup copies of their data and software and plan for recovery in the event of data loss or system problems. This promotes business continuity and data security.
- Monitoring and management: IaaS suppliers provide tools and services to monitor and control your resources and infrastructure. This includes managing VMs, storage, and network configuration using the admin panel or API, as well as measuring resource usage, automating scaling, and monitoring performance.
It is important to remember that the exact services offered by an IaaS provider may vary depending on the provider and their services. The list above shows common services from some typical IaaS providers.
Virtualized computer resources
- The infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) model of cloud computing must include virtualized computer resources. IaaS allows users to rent computer infrastructure, such as virtual machines (VMs), virtual networks, and storage, from cloud service providers over the Internet.
- In IaaS, virtual machines (VMs) are an important type of virtualized computing resource. Virtual machines (VMs), which are software simulations of real hardware, allow multiple operating systems and applications to run on a single physical host machine. Customers can choose the VM that best suits their needs from a variety of VMs with different CPU, memory, and storage configurations that IaaS providers typically offer.
- Virtual Network: Another virtualized computing resource in IaaS is the virtual network. Virtual networks allow customers to design and maintain network topologies such as subnets, IP addresses, and routing tables in the cloud. Virtual networks provide a secure, isolated environment for client applications and data, making them easy to integrate with your on-premises network.
- A major virtualized computing resource in IaaS is storage. IaaS providers often offer a variety of storage options, including block, object, and file storage, each with unique performance, pricing, and cost-effectiveness features. Storage resources are highly scalable, allowing customers to change storage capacity as needed without replacing the actual hardware.
- Virtualized computing resources are more scalable, flexible, and cost-effective than traditional on-premises hardware architectures. Customers can rent the computing power they need on-demand and pay only for what they use without investing in expensive hardware or managing their own data centers.
How does Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) work?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) customers can access resources and services over a wide area network (WAN), such as the Internet, and use the cloud provider’s services to set up the remaining elements of their application stack. For example, users can log in to an IaaS platform and create a virtual machine (VM). Install an operating system on each VM. Deploy middleware, such as databases. Create storage buckets for workloads and backups. Then install your enterprise workloads on that VM. Customers can then use the provider’s services to track costs, monitor performance, balance network traffic, troubleshoot application problems, and manage disaster recovery.
Any cloud computing model requires provider involvement. Providers are often third-party organizations that specialize in selling IaaS. Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are examples of independent IaaS providers. Businesses can also choose to become their own infrastructure service provider by deploying a private cloud.
What are the IaaS use cases?
IaaS can be used for a variety of purposes. Computing resources provided through the cloud model can be used for a wide variety of use cases. The most common use cases for IaaS deployment are:
- Test and development environment. IaaS gives organizations flexibility in terms of different testing and development environments. Easily scale up or down depending on your needs.
- Hosting of customer-facing websites. This makes hosting your website more affordable than traditional methods of hosting your website.
- Data storage, backup, and recovery. IaaS provides organizations with the easiest and most efficient way to manage data when demand is unpredictable or may constantly increase. Additionally, organizations can avoid the need for extensive efforts focused on managing data storage, legal requirements, and compliance requirements.
- Web Applications. IaaS provides the infrastructure needed to host web apps. So, if your organization is hosting a web application, IaaS can provide the necessary storage resources, servers, and networks. Deployment is quick and you can easily scale your cloud infrastructure up or down depending on the demands of your application.
- High-performance computing (HPC). Some workloads may require HPC-level computing, such as scientific calculations, financial modeling, and product design tasks.
- Data Warehousing and Big Data Analytics. IaaS provides the computing power and processing power needed to explore large data sets.
IaaS vendors and products
There are many examples of IaaS vendors and products. IaaS products from the three largest public cloud service providers, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, and Microsoft, include:
- AWS provides storage services like Simple Storage Service (S3) and Glacier and compute services like Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2).
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) provides storage and computing services through Google Compute Engine.
- Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine provides cloud virtualization for various cloud computing purposes.
These are just some of the wide range of services offered by leading IaaS providers. Services may include server less functions such as AWS Lambda, Azure Functions, and Google Cloud Functions. Access to the database. Big data computing environment. Supervision; Logging and more.
There are several other smaller or more specialized players in the IaaS market, including:
- Rackspace-managed cloud.
- IBM Cloud Pvt. Ltd.
- IBM Cloud Virtual Server.
- CenturyLink Cloud.
- Digital Ocean Droplet.
- Alibaba Elastic Compute Service.
- Alibaba Cloud Elastic High Performance Computing (e-HPC). And
- Alibaba Elastic GPU Service (EGS).
Users should carefully consider service, reliability, and cost before choosing a provider and should be able to select alternative providers and redeploy to alternative infrastructure if necessary.
Advantages of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Cloud providers offer all physical resources as a service. This means your organization doesn’t have to manage, purchase, install, or setup any resources. Users simply need access to virtual machines to build applications on top of the underlying infrastructure. It has many benefits.
- Cost-effective because organizations can lease or rent resources on demand.
- Complete control over your virtual machines.
- The infrastructure is flexible for continuous growth and enhancements, resulting in faster market entry.
- Provides scalability and control while eliminating the cost and complexity of in-house hardware deployment.
- Avoid underutilization and overuse of resources. IaaS consumers can use the appropriate amount depending on their business use case.
Disadvantages of Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS allows organizations to make better use of their budget, but even the slightest miscalculation can lead to overspending of resources. Additionally, if your cloud provider’s network experiences a problem, the downtime can impact your entire application workload.
The main drawbacks of IaaS are:
- Due to the multi-tenant nature of IaaS, resources such as bandwidth and disk space may be shared or used unequally by specific consumers (noisy neighbors), impacting overall network performance.
- Network failure occurs at the cloud vendor’s end.
- Upgradation and maintenance of infrastructure are up to the vendor.
- Providers and customers follow security guidelines, but organizations rely on providers for data security.
Related topics about cloud computing: you should know about
- Cloud Computing Reference Models: Explanation and Example with Diagrams
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing: 10 Steps to Implementation Success
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing: 6 Types, Architecture, and Advantages
- 7 Big differences between edge computing and cloud computing: Advantages and disadvantages
- Edge Computing: Definition, Concept, Uses and top 10 best practices cases in 2024
- Cloud Deployment Models: definition, types, comparisons and examples
- Top 9 Cloud Computing Platforms to know in 2024 and Advantages
- 10 Powerful Cloud Computing Applications: All you need to know
- Transforming Technology 2024: Explore the Evolution of Cloud Computing Architecture
Frequently asked question
What is an example of IaaS?
The rapid deployment speed of IaaS makes it a quick and flexible way to create and destroy development and test environments. Examples of IaaS include Rackspace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Microsoft Azure, Google Compute Engine (GCE), and Joyent.
Who uses IaaS?
Popular IaaS providers include Microsoft Azure, Amazon Web Services, Rackspace, and Google Compute Engine. Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service designed for building, testing, deploying, and managing applications and services through data centers managed by Microsoft.
Is IaaS private cloud?
Is IaaS a private cloud product? The simple answer to this question is no. IaaS does not replace or stand on par with private clouds in terms of having a suitable cloud computing solution.
What are the roles of IaaS?
IAS officers play a vital role in maintaining financial integrity, complying with regulations and contributing to the overall efficiency and accountability of ensuring government financial management at both the national and international levels.
What are three examples of IaaS?
Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Compute Engine (GCE), and IBM Cloud. Microsoft Azure.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram


6 thoughts on “Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing: advantage and disadvantages”
Comments are closed.