Software as a service (SaaS) allows users to connect to and use cloud-based apps over the Internet. Common examples include email, calendars, and Office tools (such as Microsoft Office 365).
Software as a Service (SaaS) provides a complete software solution that is purchased from a cloud service provider on a payment basis. When you rent an app for your organization, users connect to it over the Internet, usually in a web browser. The underlying infrastructure, middleware, app software, and app data all reside in the service provider’s data center. Service providers manage the hardware and software and also ensure the availability and security of your apps and data with appropriate service contracts. SaaS allows organizations to quickly get apps up and running with minimal upfront costs.
SaaS is one of the three main categories of cloud computing, along with Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) and Platform as a Service (PaaS). SaaS applications are used by a variety of IT professionals, business users, and personal users. Products range from personal entertainment, such as Netflix, to advanced IT tools. Unlike IaaS and PaaS, SaaS products are often sold to both B2B and B2C users.
Technology industry analysts predict further growth in the software-as-a-service market, with the market for SaaS products expected to reach approximately $200 billion by 2024, according to a recent report by McKinsey & Company.
Characteristics of Software as a Service (SaaS)
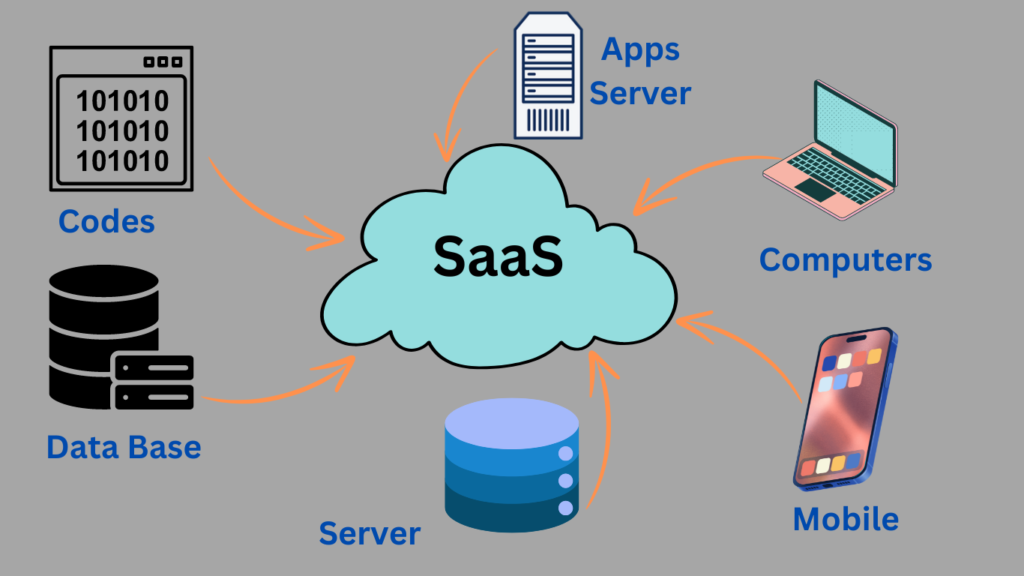
SaaS Multitenant Architecture
Multi-tenancy is an architecture in which clients and applications from all SaaS vendors share the same common infrastructure and code base that is centrally managed. This architecture allows vendors to innovate faster and save development time previously spent maintaining legacy code.
Easy Customization with SaaS
Users can easily customize the application to fit their business processes without impacting the shared infrastructure. The SaaS model supports each user’s and company’s own customizable changes and preserves them through regular upgrades. This means SaaS providers can upgrade more frequently, reducing risk and implementation costs for their customers.
Better access from network devices
The SaaS model allows businesses to access data remotely from any network-connected device, allowing them to manage permissions, monitor data usage, and allow multiple users to view the same information at the same time. .
SaaS leverages the consumer web
Amazon.com or My Yahoo! Must be familiar with web interfaces for common SaaS applications. The SaaS model allows for easy point-and-click customization, making the weeks or months it takes to update traditional business software seem frustratingly outdated.
SaaS Features of SaaS (Software as a Service)
When reducing costs and growing your business are priorities, SaaS capabilities can help your sales and business teams connect more effectively not only with existing and potential customers but also with stakeholders.
Here are the top five ways SaaS capabilities can improve your business:
- Enhance lead management by improving identification and monitoring throughout the sales cycle.
- Improve sales and marketing collaboration by better capturing and sharing prospect and customer insights.
- Improve marketing automation by streamlining digital marketing campaigns.
- Improve data management.
- Improve contact management by better storing, organizing and tracking information about your customers, and prospects.
How does software as a service work (SaaS)?
SaaS works through a cloud delivery model. Software providers may be ISVs that use their own servers, databases, networking, and computing resources to host applications and related data, or that contract with cloud providers to host applications in the provider’s data centers. We do. The application can be accessed from any device with a network connection. SaaS applications are typically accessed through a web browser.
As a result, companies using SaaS applications no longer need to be responsible for software setup and maintenance. Users simply pay a subscription fee to access the software, which is a ready-made solution.
SaaS is closely related to the application service provider (ASP) and on-demand computing software delivery models, where the provider hosts the customer’s software and delivers it to authorized end users over the Internet.
In the software-on-demand SaaS model, a provider provides customers with network-based access to a single copy of an application that the provider has created specifically for SaaS delivery. The application source code is the same for all customers, and as new features are released, they are rolled out to all customers. Depending on the service level agreement (SLA), customer data for each model can be stored locally, in the cloud, or both locally and in the cloud.
Organizations can use application programming interfaces (APIs) to integrate SaaS applications with other software. For example, companies can write their own software tools and use the SaaS provider’s API to integrate those tools with SaaS products.
SaaS (Software as a Service) architecture
SaaS applications and services typically use a multi-tenant approach. This means that a single instance of the SaaS application runs on a hosted server, and that single instance provides service to each subscription customer or cloud tenant. Applications run with the same version and configuration for all customers or tenants. Customers with different subscriptions run on the same cloud instance with the same infrastructure and platform, but the data of different customers remains separate.
The multi-tenant architecture typical of SaaS applications means that cloud service providers can manage maintenance, updates, and bug fixes faster, easier, and more efficiently. Engineers can make necessary changes to all customers by maintaining a shared instance rather than applying changes to multiple instances.
Additionally, multi-tenancy makes more resources available to more clusters without compromising critical cloud features like security, speed, and privacy.
Advantages of SaaS (Software as a Service)
SaaS eliminates the need for organizations to install and run applications on their own computers or in their own data centers. This eliminates the costs of purchasing, provisioning, and maintaining hardware, as well as software licensing, installation, and support. Other benefits of the SaaS model include:
- Flexible payment. Customers subscribe to SaaS services rather than purchasing software to install it or additional hardware to support it. By shifting costs into recurring operating expenses, many companies are able to create better and more predictable budgets. Users can terminate the SaaS service at any time to prevent recurring costs.
- Scalable usage. Cloud services like SaaS offer high vertical scalability, giving customers the option to access more or fewer services and features on demand.
- Automatic updating. Instead of purchasing new software, customers can rely on SaaS providers to automatically manage updates and patches. This reduces the burden on in-house IT staff.
- Reach and persistence. SaaS vendors deliver applications over the Internet, so users can access them from any Internet-enabled device or location.
- Adaptation. SaaS applications are often customizable and can be integrated with other business applications, especially those from general software providers.
Disadvantages of SaaS (Software as a Service)
Despite all the benefits of SaaS software, there are some drawbacks for users and businesses that choose such services.
Interruption or downtime
Even the largest and most effective software programs can experience problems that can cause service interruptions and software downtime. Large companies could experience disruption, reduced productivity, and administrative and financial losses as a result of this type of disruption.
Advanced Access Control
Anyone with valid credentials can access SaaS apps over the Internet, so it’s important to ensure there’s an adequate level of identity verification in place for your organization and your users. This is important because organizational data is now stored online on remote SaaS servers rather than on the local network.
Lack of vendor flexibility
This is another problem that businesses adopting SaaS services may face. Switching to a new service provider can be difficult and time-consuming, as existing company databases and information must be transferred from the old program to the new program.
Less control
New features can be added if application developers decide to patch or upgrade their current software to improve performance. Even if there is additional expense to train employees to adapt to the changes, the company usually has little say about whether such updates are feasible.
Security Concerns
SaaS cloud security is completely managed by the service provider, which can be a challenge for some businesses that prefer to handle and protect their data according to their own security policies.
Popular SaaS Service Providers
The SaaS market includes a variety of software vendors and products. Industry players range from small single-product vendors to cloud giants like AWS and Google.
SaaS products also range from video streaming services to IT business analytics tools. There are SaaS applications for basic business applications like email, sales management, customer relationship management (CRM), financial management, human resource management (HRM), billing and collaboration. Enterprise SaaS products for a specific industry, such as insurance or healthcare, are called vertical SaaS products.
- Salesforce
- Google Workspace apps
- Microsoft 365
- HubSpot
- Trello
- Netflix
- Zoom
- Zendesk
- DocuSign
- Slack
- Adobe Creative Cloud
- Shopify
- Mailchimp
Related topics about cloud computing: what you should know about
- Cloud Computing Reference Models: Explanation and Example with Diagrams
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing: 10 Steps to Implementation Success
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) in cloud computing: advantage and disadvantages
- What is Platform as a Service (PaaS)? Advantages and disadvantages
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing: 6 Types, Architecture, and Advantages
- 7 Big differences between edge computing and cloud computing: Advantages and disadvantages
- Edge Computing: Definition, Concept, Uses and top 10 best practices cases in 2024
- Cloud Deployment Models: definition, types, comparisons and examples
- Top 9 Cloud Computing Platforms to know in 2024 and Advantages
- 10 Powerful Cloud Computing Applications: All you need to know
- Transforming Technology 2024: Explore the Evolution of Cloud Computing Architecture
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram


3 thoughts on “What is SaaS (Software as a Service)? Advantages and disadvantages”
Comments are closed.