What is computer security?
Computer security refers to the protection of computers and their associated data, networks, software and hardware from unauthorized access, misuse, theft, information loss and other security problems. Although the Internet has made our lives easier and brought us many benefits, it has also exposed the security of our systems to risks such as virus infection, hacking, information theft and damage to our systems.
Technology is increasing day by day and the whole world is in its grip. We cannot even imagine a day without electronic devices around us. Using this growing technology, intruders, hackers, and thieves are attempting to use our services for financial gain, support purposes, demanding ransom, threatening others, infiltrating other businesses and organizations, and compromising the security of your computer. With these risks in mind, computer security is important.
Computer security is concerned with protecting computer systems and information from loss, theft, and unauthorized use. The main reason users are repeatedly attacked is that they lack adequate security to stop intruders, and cyber criminals are quick to exploit such vulnerabilities. Computer security ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of computers and the data they store.
Types of Computer Security
- One way to look at the similarities and differences in computer security is to ask what is being protected. For example,
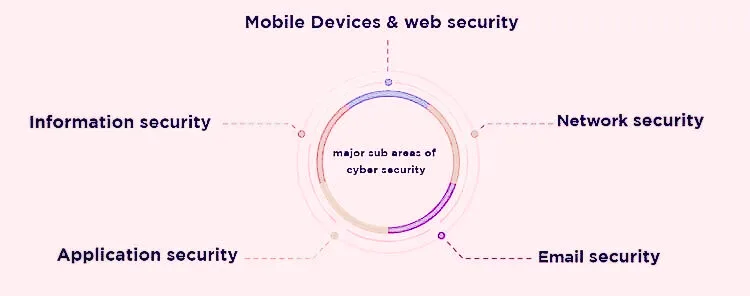
- Information security is the protection of information from unauthorized access, modification, or deletion.
- Application security protects applications by building security features to prevent cyber threats such as SQL injections, DoS attacks, and data breaches.
- Computer security means keeping standalone machines updated and patched to ensure security.
- Network security is achieved by securing both software and hardware technologies.
- Cyber security is defined as the security of computer systems communicating over computer networks.
Computer security can be classified into four types:
Cyber Security
Internet security is a modern type of computer security that has recently experienced a boom period. It is a way to create a complete set of rules and actions to prevent unauthorized access and damage to computer systems directly connected to the Internet.
It is a modern field of computer security that specifically addresses risks and threats associated with the Internet, such as:
- Hacking
- Computer viruses
- Malware
- Denial of service attacks
Cyber security refers to protecting computers, electronic devices, networks, programs and systems from cyber attacks. A cyber attack is an attack that occurs when a system is connected to the Internet.
Information Security
Information security is a type of cybersecurity that focuses on methods and techniques specifically designed to ensure the security of computers. Information security as a process was developed to protect the availability, integrity and confidentiality of computer systems from data theft, unauthorized access, damage and destruction. Information security means protecting the information in your system from theft, illegal access and unauthorized access. Information security has three main objectives: information confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Information security is commonly known as the CIA Triad, and this model is used to protect the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of organizational data to maintain productivity.
Application Security
When security features are introduced early in the development process, it is called application security. It is highly capable of protecting computer systems from cyber-security threats such as unauthorized access and data breaches. Additionally, it helps protect computer systems from SQL violations and denial-of-service attacks. Application security means protecting your applications and data from being hacked. Additionally, the application’s database is secure and private to the owner, meaning user data remains private.
Some key application tool technologies, such as software encryption, antivirus, and firewalls, are used to establish application security features that help the system build a bulwark against cyber attacks.
Network Security
Network security, as the name suggests, is another type of computer security that protects computer systems from unauthorized intrusion and access to the computer network. It is similar to information security in that it also protects the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of computer networks. Network security is designed with multiple configurations to achieve maximum performance. This includes both software and hardware security.
A variety of network security methods and components exist to ensure the security of computer networks. These are described as follows:
- Application security
- Anti-virus software
- Behavioral analysis
- Firewall
- Email security
- Web security
- Wireless security
- Network access control
- Network segmentation
- Virtual private network
Network security means securing your network and protecting information about users connecting to that network. Hackers steal packets of data on the network through sniffing, spoofing attacks, man-in-the-middle attacks, and war driving and exploit the data to their advantage.
Endpoint Security
Errors made by humans can easily be taken advantage of by hackers and cyber criminals. End users in any organization face significant security risks. End users become victims of cyber crimes due to lack of knowledge about IT security and policies. Because they are less aware, they may unknowingly give cyber criminals access to their computer systems.
Therefore, it is important to understand comprehensive security policies and procedures to stay alert and avoid falling into the trap of cyber criminals. Awareness training programs should be planned to increase knowledge about computer security and its threats.
Types of cyber attack
Denial of service attack, or DOS:
Denial of service is a type of attack in which an attacker disrupts the service of a particular network by sending endless requests and making network or machine resources temporarily or permanently unavailable to intended users.
Backdoor
In a backdoor attack, malware, trojans, and viruses get installed on your system and start affecting key files as well as your security. Let us consider an example. Suppose you are installing free software from a particular website on the internet. Along with this software, a malicious file also gets installed unknowingly, and as soon as you run the installed software, the malware present in that file gets affected and starts affecting the security of your computer. This is known as the backdoor.
Eavesdropping
Eavesdropping means listening to someone secretly without their permission or knowledge. Attackers attempt to steal, manipulate, modify, or hack information or systems by passively learning network communications or passwords. As a physical example, consider a third party listening to your private conversation while you are talking to someone else in your organization. It is said that if you speak, he will hear your conversation. Similarly, conversations on the Internet can be eavesdropped on on by attackers who may be monitoring your private conversations by connecting to your network if it is not secure.
Phishing
Phishing is pronounced “phishing” and has the same function. When fishing, you use bait to attract fish. Similarly, in phishing, users are deceived and their information is stolen by an attacker who gains their trust or pretends to be a real person. Apart from attackers, some websites that appear to be genuine are actually fraudulent sites. These sites trick users into providing personal information such as login details, bank account details and card numbers. There are many types of phishing, including voice phishing and text phishing.
Spoofing
Spoofing is the act of altering data (such as an IP address or username) to impersonate a legitimate entity in order to access information or resources that you are not authorized to obtain. There are many types of spoofing, including email spoofing, IP address spoofing, MAC spoofing, and biometric spoofing.
Malware
Malware consists of two words: malicious + software = malware. Malware is designed to invade your system and cause damage to your computer. There are many types of malware, including adware, spyware, ransomware, and Trojan horses.
Social engineering
Social engineering attacks involve extracting sensitive data from users by psychologically manipulating them and gaining their trust. Attackers typically rely on the cognitive foundations of people and users to exploit their trust.
Polymorphic Attacks
Poly means “many” and morph means “shape,” and a polymorphic attack is one in which an attacker adopts multiple shapes and changes them, making them difficult to detect. This type of attack is difficult to detect because its form keeps changing.
Steps to ensure computer security
To protect their system from the above attacks, users need to take certain steps to ensure system security.
- Keep your operating system updated. Keeping it updated reduces the risk of getting attacked by malware, viruses, etc.
- Always use a secure network connection. You should always be connected to a secure network. Avoid using public Wi-Fi or unsecured networks, as they may be vulnerable to attacks from attackers.
- Always install antivirus software and keep it updated. Antivirus software scans your PC for viruses and isolates infected files from other system files so that they remain unaffected. Also, make sure to use paid antivirus software, which is more secure.
- Enable your firewall. A firewall is a system designed to prevent unauthorized access to your computer as well as your computer’s private network. Firewalls may include hardware, software, or a combination of both.
- Use strong passwords. Always create strong and unique passwords for all your social media accounts to prevent easy identification through key recording, brute force, and dictionary attacks. A strong password is a 16-character password that includes a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Also, please change your password regularly.
- Don’t trust people easily. You never know someone’s intentions. Therefore, please do not trust others easily and entrust your personal information to others. You don’t know how they will use your information.
- Keep your personal information private. Do not post all your personal information on social media. You never know who is spying on you. Just like in the real world, we try to avoid talking or sharing things with strangers. Similarly, there are people on social media you don’t know, and if you share all your information there, you could get yourself into trouble.
- Do not download attachments from emails unless you know that the email is from the original source. Most of the time, these attachments contain malware that infects or damages your system when executed.
- Do not buy goods online from anywhere. When shopping online, make sure you buy from reputable websites only. There are many fraudulent websites that will steal your card information as soon as you check out, potentially bankrupting you.
- Learn about computer security and ethics. Become familiar with secure computing and the ethics of the computing industry. Having proper knowledge always helps in reducing cybercrime.
- If you are attacked, please inform the cyber cell immediately. The cyber cell can then take appropriate measures to protect others from attacks by the same person. Don’t be afraid to complain just because people may find you funny.
- Do not use pirated content. People often try to download pirated movies, videos, or web series to get them for free. These pirated materials have a high risk of being infected with viruses, worms, or malware, and downloading them will put the security of your system at risk.
Important topics about cyber security. You should know:
- Ransomware Definition: 6 Types of Variants, Attacks, and How to Prevent?
- 12 types of Phishing attacks: Prevention, causes, techniques and examples
- What is malware? History, Definition, 7 main types and real-world examples
- 3 Main Objectives of Cybersecurity
- Cybersecurity Goals: 3 major objectives of cybersecurity
Frequently Ask Questions
Question 1. What are the types of computer security?
Computer security is of four types:
- Cyber Security
- Information Security
- Application Security
- Network Security
Question 2: What is cyber security?
Cyber security refers to the protection of computers, electronic devices, networks, programs and systems from cyber attacks. A cyber attack is an attack that occurs when a system is connected to the Internet.
Question 3. What is social engineering?
Social engineering attacks extract sensitive data from users by psychologically manipulating them and gaining their trust. Attackers typically rely on the cognitive infrastructure of people and users to exploit that trust.
Question 4. What steps can be taken to ensure computer security?
- Always keep your Operating System up to date.
- Always use a secure network connection.
- Always install an Antivirus and keep it up to date.
- Enable firewall.
Question 5. What is an antivirus? Name some antivirus software.
Antivirus software scans your PC for viruses and isolates infected files from other system files so that they remain unaffected. Also, make sure to use paid antivirus software, which is more secure.
Some of the antivirus programs are: Quickheal, Norton, F-Secure, and Kaspersky.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram


1 thought on “5 types of Computer security: definitions, Importance, Threats, and best examples in 2024”
Comments are closed.