Introduction
Cryptography is the most common way of stowing away or coding data, so only the individual for whom a message was expected can understand it. The craft of cryptography has been utilized to code messages for millennia and keeps on being utilized in bank cards, PC passwords, and web-based businesses.
Cryptography is the investigation of getting interchanges from outside eyewitnesses. Encryption calculations take the first message, or plaintext, and change it into ciphertext, which isn’t reasonable. The key permits the client to decode the message, hence guaranteeing that they can peruse the message. The strength of the arbitrariness of an encryption is additionally examined, which makes it harder for anybody to figure out the key or contribution of the calculation. Cryptography is the way we can accomplish safer and more vigorous associations while raising our security. Headways in cryptography make it harder to break encryptions, so scrambled documents, envelopes, or organization associations are simply available to approved clients. Cryptography focuses on four different objectives:
Confidentiality
Confidentiality means that only the intended recipient can decrypt the messages and read the content.
Non-repudiation
Non-disavowal implies the source of the message can’t backtrack from here on out and deny their purposes behind sending or making the message.
Integrity
Uprightness centers around the capacity to be sure that the data held inside the message can’t be altered while away or traveling.
Authenticity
Credibility guarantees the source and beneficiary can check each other’s personalities and the objective of the message.
History of cryptography
Codes and codes have been utilized to send and get secret directives for millennia. Coded symbolic representations and cuneiform engravings from antiquated Egypt and Babylon are the earliest enduring instances of “old style” cryptography that pre-owned replacement strategies to make an interpretation of plaintext into ciphertext, and back once more.
These somewhat straightforward, manual cryptographic methods remained in a general sense unaltered for many years until the mid-twentieth century introduced another time of cryptography, with complex electromechanical machines empowering more refined and proficient coding and unraveling processes. Albeit the appearance of advanced registering innovation sped up this pattern, cryptography has taken another quantum jump forward in a long time with the creation of public-key cryptography that utilizes computerized signature and disseminated confirmation innovation. This has brought about drastically further developed encryption conventions; however, it has likewise empowered the inescapable individual and business utilization of cryptography.
Types of cryptography
There are three cryptography types, which are recognized by the sorts of cryptographic calculations they use to scramble information. Most sorts of cryptography use calculations called keys that scramble and unscramble, or code and translate, information.
Here are the various sorts of cryptography:
- Secret Key Cryptography: A secret key is utilized to both scramble and unscramble the information. The source remembers the mystery key for the coded message shipped to the expected beneficiary. Assuming that the message is caught, the included key can disentangle its items.
- Public Key Cryptography: The source utilizes a public key to scramble the message, and the collector utilizes a confidential key to unscramble it. Assuming the message is captured, the items can’t be translated without the confidential key.
- Hash Capabilities: Hash capabilities don’t depend on keys. All things being equal, they scramble information about changing sizes into upsides of uniform length. With hash capabilities, both a single-word message and a 1000-page novel make a fixed-sized result of the encoded message (called a hash esteem), making it almost impossible to decide the first happy. Generally utilizing the MD5 hashing calculation, hashing is frequently utilized for confirmation purposes.
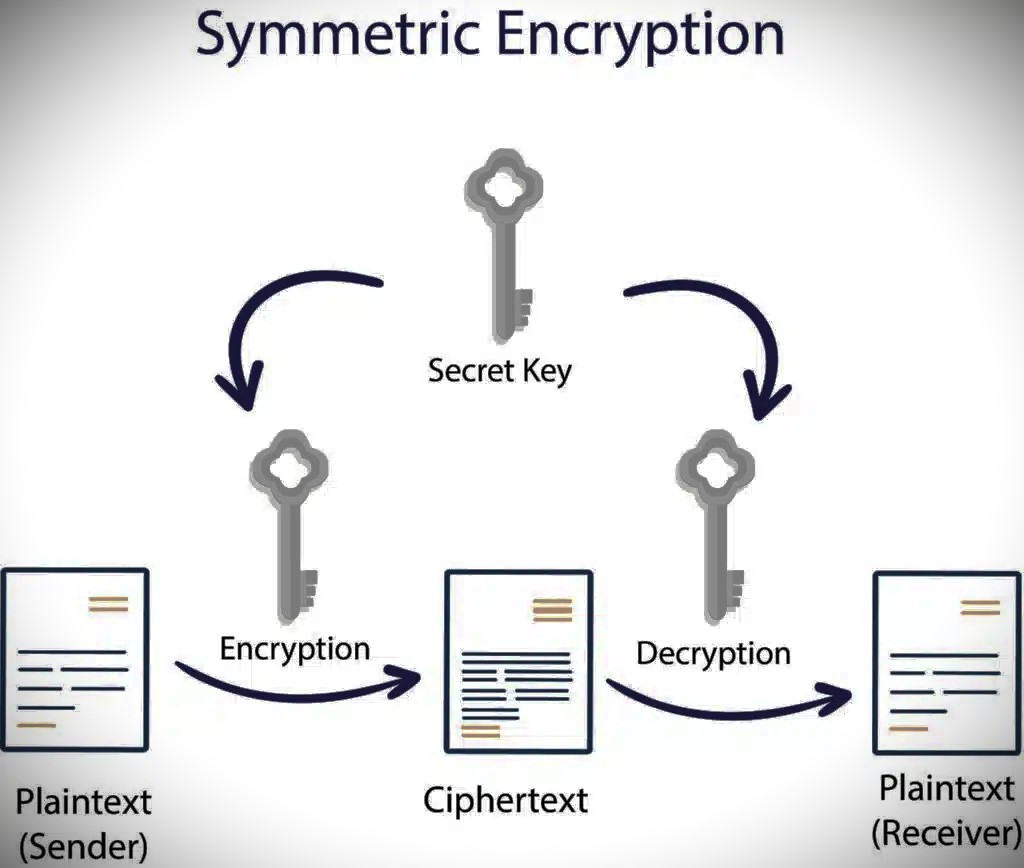
Examples:
- AES
- DES
- Caesar Cipher
Public key cryptography, or unbalanced cryptography, utilizes two keys to scramble information. One is utilized for encryption, while the other key can decode the message. In contrast to symmetric cryptography, assuming one key is utilized to encode, that equivalent key can’t decode the message; rather, the other key will be utilized.
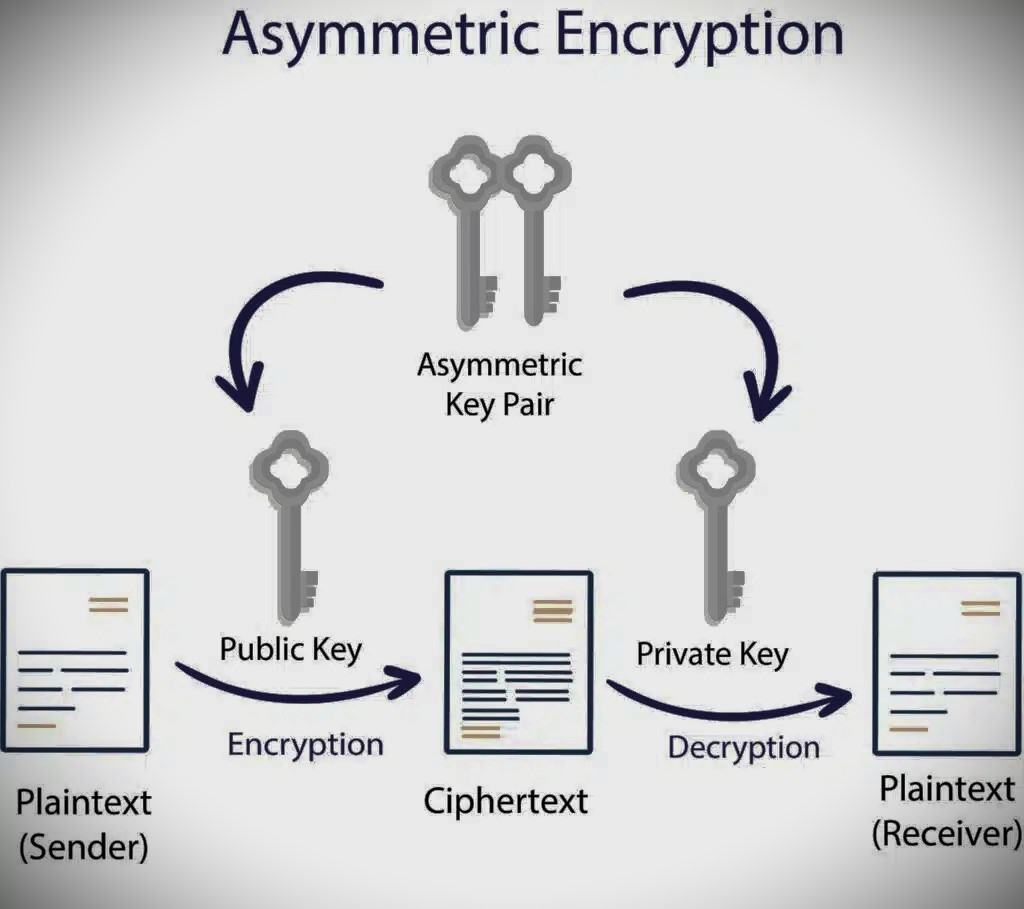
One key is kept hidden and is known as the “confidential key,” while the other is shared freely and can be utilized by anybody; consequently, it is known as the “public key.” The numerical connection of the keys is to such an extent that the confidential key can’t be gotten from the public key, yet the public key can be gotten from the private key. The confidential key ought not to be dispersed and ought to stay with the proprietor, as it were. The public key can be given to some other element.
Examples:
- ECC
- Diffie-Hellman
- DSS
A hash function is an immutable, one-way function that protects data at the cost of not being able to recover the original message. Hashing is a method of converting a given string into a fixed-length string. A good hashing algorithm produces a unique output for each given input. The only way to crack a hash is to try all possible inputs until you get exactly the same hash. Hashes can be used to hash data (such as passwords) and certificates.
Some of the most famous hashing algorithms are:
- MD5
- SHA-1
- SHA-2 family which includes SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512
- SHA-3
- Whirlpool
- Blake 2
- Blake 3
How does cryptography work?
Encryption works by taking plaintext (or cleartext) and scrambling it into ciphertext, making the encoded output understandable only by the intended recipient. The information must be in cryptographic form and cannot be read by anyone other than the intended recipient.
In cybersecurity, encryption is typically used to transform plaintext into ciphertext, while decryption reverses that process. The best encryption software uses complex cryptographic algorithms that are extremely difficult to crack.
The exact technique used to convert plaintext to ciphertext defines how encryption works. Symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption, blockchain, and digital signatures are some of the major cryptographic techniques. Hashing, another encryption process, does not use a key, so it is not technically encryption.
Learn More About Cybersecurity Topics:
Cryptography vs encryption
The difference between encryption and cryptography is that cryptography can be broadly defined as the science of sending secret messages, whereas encryption is a specific process of converting data into codes. Although encryption is an integral part of cryptography, it is only one part of a more complex set of cryptographic elements required to transmit information securely.
Use of cryptography
Encryption is used to keep communications and information confidential. Keeping your data secure with encryption reduces threats like ransomware attacks because even if a hacker intercepts your information, they won’t be able to decipher it without the decryption key.
Here are some common uses of encryption:
- Financial Transactions and Online Banking: Online banking and e-commerce websites use advanced encryption technology to keep your financial information secure.
- SSL-secured websites: Websites with an SSL certificate create a secure, encrypted connection to protect the information sent from your browser to the website’s server.
- VPN: A VPN is a security tool that redirects your web traffic through a private server and encrypts your connection.
You can enable Wi-Fi encryption in your router settings, but if privacy and security are really important to you, you need a VPN. VPN encryption methods vary depending on the VPN protocol used. For example, the WireGuard VPN protocol is one of the newest, while the OpenVPN protocol is probably the most popular.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram


3 thoughts on “10 Best Real-World Examples of Cryptography You Use Daily”
Comments are closed.