Definition of Virtualization
Virtualization in cloud computing can be defined as a process that allows the creation of virtual versions of desktops, operating systems, network resources, or servers. Virtualization plays an important and major role in cloud computing.
This ensures that the physical delivery of a resource or application is separate from the actual resource. Helps in reducing the space and cost associated with resources. This technology allows end users to run multiple desktop operating systems and applications simultaneously on the same hardware and software.
This process ensures the virtual emulation of products and services within a single machine without slowing down the system or affecting its efficiency.
The invention of virtualization began in the era of mainframe use, and with the advancement of new-age technologies over time, virtualization was achieved using specialized software.
Virtualization is the technique of separating a service from its underlying physical delivery. It is the process of creating a virtual version of something, such as computer hardware. It was originally developed during the mainframe era. It involves using specialized software to create a virtual or software-created version of a computing resource instead of a real version of the same resource. With the help of virtualization, multiple operating systems and applications can be run simultaneously on the same machine and its hardware, thereby increasing hardware utilization and flexibility.
In other words, one of the main cost-effective, hardware-reducing, and energy-saving technologies used by cloud providers is virtualization. Virtualization allows a single physical instance of a resource or application to be shared among multiple customers and organizations simultaneously. This is done by assigning a logical name to the physical storage and providing a pointer to that physical resource on demand. The term virtualization is often synonymous with hardware virtualization and plays a fundamental role in efficiently delivering infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) solutions for cloud computing. Additionally, virtualization technology provides a virtual environment for running applications as well as storage, memory, and networking.

- Host Machine: The machine on which the virtual machine is created is called the host machine.
- Guest Machine: A virtual machine is called a guest machine.
Virtualization in Cloud Computing: A Basic Concept
In cloud computing, virtualization facilitates the creation of virtual machines and ensures the smooth functioning of multiple operating systems. It also helps in creating a virtual ecosystem of server operating systems and multiple storage devices to run multiple operating systems.
Cloud computing is considered as an application or service that comprises a virtual ecosystem. Such ecosystems may be public or private in nature. Virtualization reduces the need for physical infrastructure. The terms cloud computing and virtualization are now used interchangeably and are becoming increasingly integrated.
Virtualization and cloud computing work together to ensure advanced levels of computing sophistication. This allows applications to be shared across multiple network threads from different companies and active users.
Cloud computing provides scalability, efficiency, and economic value. Provides a streamlined workload management system.
Simply put, cloud computing and virtualization together ensure that modern businesses have a more cost-effective way to run multiple operating systems using a single dedicated resource.
Some interesting topics about cloud computing that you should know
Work of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization has a significant impact on cloud computing. In case of cloud computing, users store their data in the cloud, but with the help of virtualization, users get the added benefit of sharing the infrastructure. Cloud vendors handle the physical resources required, but these cloud providers charge heavy fees for these services, which impacts each user or organization. Virtualization helps a user or organization maintain essential services for the enterprise through external (third-party) personnel, which helps reduce costs for the enterprise. This is how virtualization works in cloud computing.
Benefits of Virtualization
- More flexible and efficient allocation of resources.
- Improvement in development productivity.
- Reduces IT infrastructure costs.
- Remote access and rapid scalability.
- High availability and disaster recovery.
- Pay on-demand to view IT infrastructure.
- Enables the running of multiple operating systems.
Disadvantages of virtualization
- High initial investment: Cloud computing involves a very high initial investment, but it is also true that it can lead to cost savings for businesses.
- Learning new infrastructure: As companies move from servers to the cloud, they need highly skilled employees with the skills to easily navigate the cloud, which can be achieved by hiring new employees or providing training to existing employees. Can be refinanced.
- Data Risk: Hosting your data on third-party resources can put your data at risk and can be easily attacked by hackers and crackers.
Types of Virtualization in cloud computing
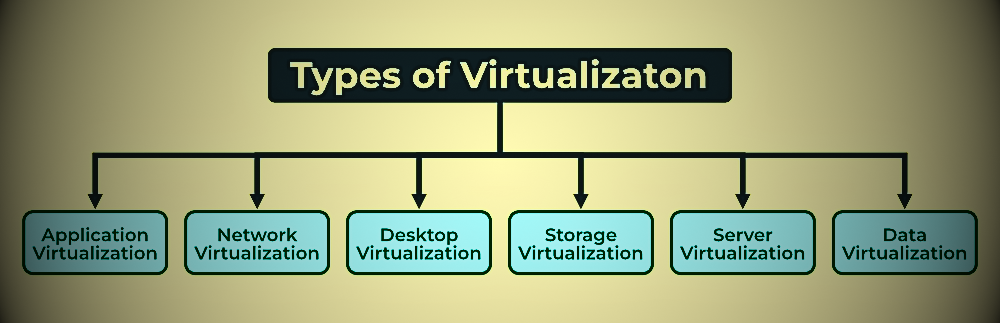
- Application Virtualization
- Network Virtualization
- Desktop Virtualization
- Storage Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Data virtualization
Application Virtualization
Application virtualization allows users to remotely access applications from the server. The server stores all your personal information and other features of the application, but it can also be run on your local workstation via the Internet. An example of this is a user who needs to run two different versions of the same software. Technologies that use application virtualization include hosted applications and packaged applications.
Network virtualization
The ability to run multiple virtual networks, each with different control and data plans. Co-exist on a physical network. It may be managed by different parties, which may be mutually confidential. Network virtualization provides the ability to create and provision virtual networks, logical switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers, virtual private networks (VPNs), and workload protection within days or weeks.
Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization allows you to remotely store a user’s OS on a server in your data center. It allows users to access their desktop virtually from any location using another machine. Users who require a specific operating system other than Windows Server will need a virtual desktop. The main benefits of desktop virtualization are user mobility, portability, and easy management of software installation, updates, and patches.
Storage Virtualization
Storage virtualization is a series of servers managed by a virtual storage system. The server does not know exactly where the data is stored; rather, it acts like a worker bee in a hive. It allows storage from multiple sources to be managed and used as a single repository. Storage virtualization software maintains smooth operation, consistent performance, and a consistent suite of advanced features despite changes, failures, and differences in the underlying equipment.
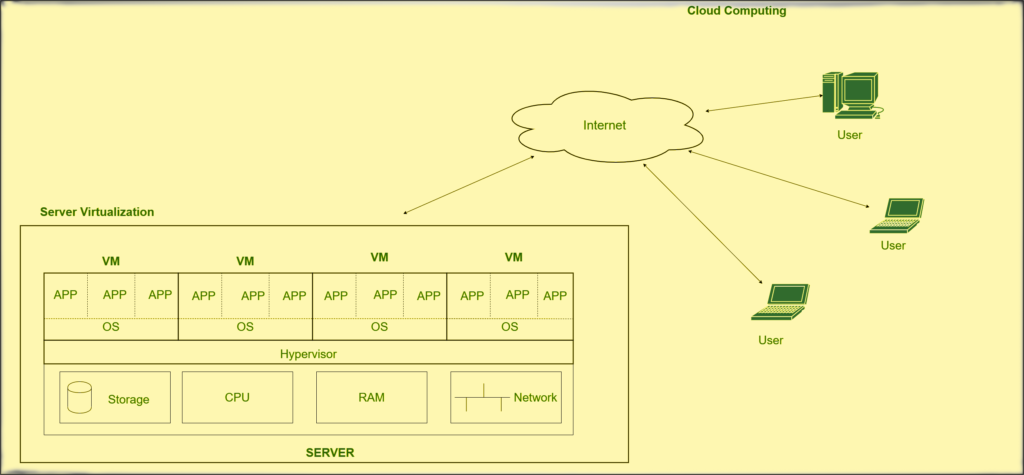
Server Virtualization
This is a type of virtualization where the masking of server resources is done. Here, a central server (physical server) is divided into many different virtual servers by changing their identification numbers and processors. Therefore, each system can run an operating system independently. When each subserver knows the identity of the central server,. Deploying the resources of the main server to subserver resources improves performance and reduces operating costs. This helps in virtual migration, reducing energy consumption, reducing infrastructure costs, and much more.
Data Virtualization
It is the process of collecting data from various sources without knowing the detailed technical information, such as how the data is collected, stored, formatted, and logically organized, so that a virtual view displays which virtual machines are collected and managed in one place. Stakeholders, stakeholders and users can access it remotely through various cloud services. Many giants like Oracle, IBM, Atscale, and Cdata provide their services.
Architecture of Virtualization
An architecture in virtualization is defined as a model that conceptually describes virtualization. Virtualization applications are important in cloud computing. In cloud computing, end users share data over an application called a cloud. However, end users can share their entire IT infrastructure with virtualization as well.
The virtualization architecture is:
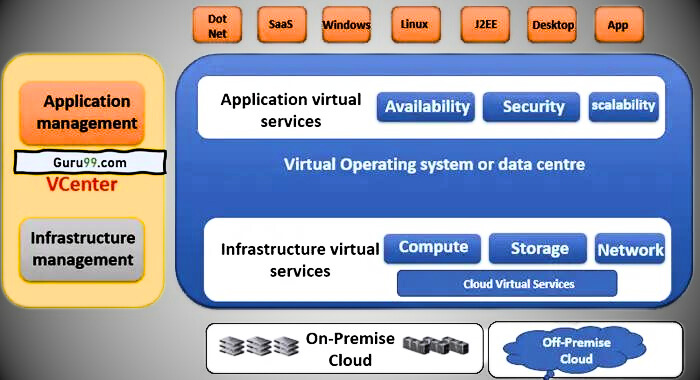
- In the diagram above, virtualization includes virtual applications and infrastructure virtual services.
- Virtual Application Services helps with application management, and Virtual Infrastructure Services helps with infrastructure management.
- Both services are built into a virtual data center or operating system. Virtual services can be used on any platform and in any programming environment. Services can be accessed on-premises or off-premises through the cloud.
- Virtualization services are provided to cloud users by third-party individuals. Instead, cloud users must pay an applicable monthly or annual fee to the third party.
- This fee is paid to compensate third parties for providing cloud services to end users. Third parties also offer different versions of their applications, depending on the needs of end-user cloud users.
- Virtualization is typically achieved through a hypervisor. A hypervisor allows you to separate the operating system from the underlying hardware. This allows a host machine to run multiple virtual machines simultaneously and share the same physical computer resources.
There are two ways to achieve a virtualized architecture:
- Type 1: The first type of hypervisor is called a bare metal hypervisor. They run directly on the hardware of the host system. These provide effective resource management and ensure the high availability of resources. It provides direct access to the hardware system, ensuring better scalability, performance, and stability.
- Type 2: The second hypervisor type is a hosted hypervisor. It is installed on the host operating system, and the virtual operating system runs directly on top of the hypervisor. It is a system that makes system creation convenient and simple.
Also, administrative tasks become simpler. The presence of a host operating system can limit the performance of virtualization-enabled systems and may also introduce security vulnerabilities and risks.
Advantages of Virtualization
The advantages/benefits of virtualization are:
- Virtualization offers many benefits, including reducing costs and increasing productivity in the development process.
- Eliminates the need for overly complex IT infrastructure.
- Ensures easy remote access to resources and fast scalability.
- Highly flexible, allowing users to run multiple desktop operating systems on the same standard machine.
- Eliminates the risks associated with system failure and also enhances flexible data transfer between different virtual servers.
- Virtualization work processes are highly streamlined and agile, allowing users to work and operate in the most economical manner.
Disadvantages of Virtualization
The disadvantages of virtualization are very limited in nature. The advantages and disadvantages of virtualization are:
- Migration from an existing hardware setup to a virtualized setup requires a significant investment of time, so it can be considered a time-consuming process.
- Lack of skilled resources to assist in transitioning from an existing or physical setup to a virtual setup.
- Virtualization implementation requires high costs due to limitations in terms of a lack of skilled resources.
- There is also a security risk to sensitive data if the migration process is not handled with the utmost care.
Role of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
Virtualization provides a suitable name for the physical servers. The pointer is then pointed to that physical server, which is served on demand. Virtualization makes it easier to run homogeneous applications.
It also provides a virtual and isolated network, storage and memory space environment. Virtualization is achieved through host machines and guest machines. A host machine can be defined as a machine on which a virtual machine is developed, and such a developed virtual machine is called a guest machine.
Hardware virtualization plays a vital role under cloud computing processes by providing infrastructure-as-a-service solutions in the most efficient and effective manner.
This type of virtualization ensures portability. Guest machines are packaged as virtual instances of images, and such virtual images can be easily removed when needed.
Important Terminologies of Virtualization
There are several essential technologies for virtualization, defined as:
- Virtual Machine: A virtual machine can be defined as a virtual type of computer that runs under a hypervisor.
- Hypervisor: It can be defined as an operating system that runs on the actual hardware. A virtual counterpart of an operating system is a subpart that runs or simulates a virtual process. These are defined as Domain 0, or Dom0.
- Containers: These can be defined as lightweight virtual machines that are a subset of the same operating system instance or hypervisor. These are collections of processes that run with associated namespaces or process identifiers.
- A virtual network is defined as a logically isolated network that exists within a single server. This type of network can be extended to multiple servers.
- Virtualization software: This type of software helps to deploy virtualization on computing devices.
Uses of Virtualization
- Data-integration
- Business-integration
- Service-oriented architecture data-services
- Searching organizational data
Summary
- Virtualization helps in creating virtual versions of desktops, servers, operating systems, and applications.
- Virtualization includes host machines and virtual machines.
- Every virtualized system consists of a hypervisor, containers, and virtual networks.
- Virtualization increases efficiency and scalability and helps in effective resource management.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram


6 thoughts on “Virtualization in Cloud Computing: 6 Types, Architecture, and Advantages”
Comments are closed.