OpenStack cloud architecture is a component of several open-source projects. These projects are used to set up the OpenStack, which is under cloud or overcloud. Under the cloud is the core component, which is managed by the system admin for the end user.
Introduction of OpenStack
OpenStack cloud architecture is a free, open-source cloud computing platform that was first introduced on July 21, 2010. Rackspace Hosting and NASA were creating a joint project for cloud computing. It is deployed in Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS) for both public and private clouds. Hardware support like processing, storage, and networking resources is managed by the data center and controlled by third-party vendors. A software platform tool that is used in OpenStack is called “Projects.” These projects handle multiservices like computing, networking, and storage services. RAM, CPU, and other hardware resources in the virtualization are managed by the hypervisor.
Features of OpenStack Cloud Architecture
Modular Architecture
OpenStack is designed with a modular architecture where users can deploy the components on demand. It provides the ability to customize the platform for specific business requirements.
Multi-tenancy support
It means multiple users can access the same cloud infrastructure while security maintenance and isolation are running.
Open-source software
OpenStack is an open-source platform that is free to use and modify. Users can customize the platform for specific requirements without any charges.
Distributed architecture
OpenStack is designed with a distributed architecture so that users can design and manage the architecture on multiple physical servers. This is useful to handle workloads and improve system performance.
Compute (Nova)
This feature includes managing the large networks of virtual machines and providing scalable computer resources.
Storage (Swift and Cinder)
Swift and Cinder belong to storage and block storage. OpenStack cloud provides the Swift and Cinder facility for object storage, provides data flow smoothly, and retrieves the data easily.
6 Differences: Block Storage vs. Object Storage: benefits and uses
Network (Neutron)
It manages IP addresses, balances internet traffic, and ensures internet security. It manages the complex network.
Orchestration (Heat)
It deploys and simplifies the infrastructure of cloud management automatically.
Identity
It provides the authentication and authorization of OpenStack components and ensures the access control of data.
Dashboard
It provides the web-based user interface of OpenStack. The user can easily access and manage the OpenStack account from a browser in a cloud environment. Bare Metal: It allows the provisioning of the physical machine, and the user can expand the utility on the OpenStack cloud.
7 Components of OpenStack Cloud Architecture
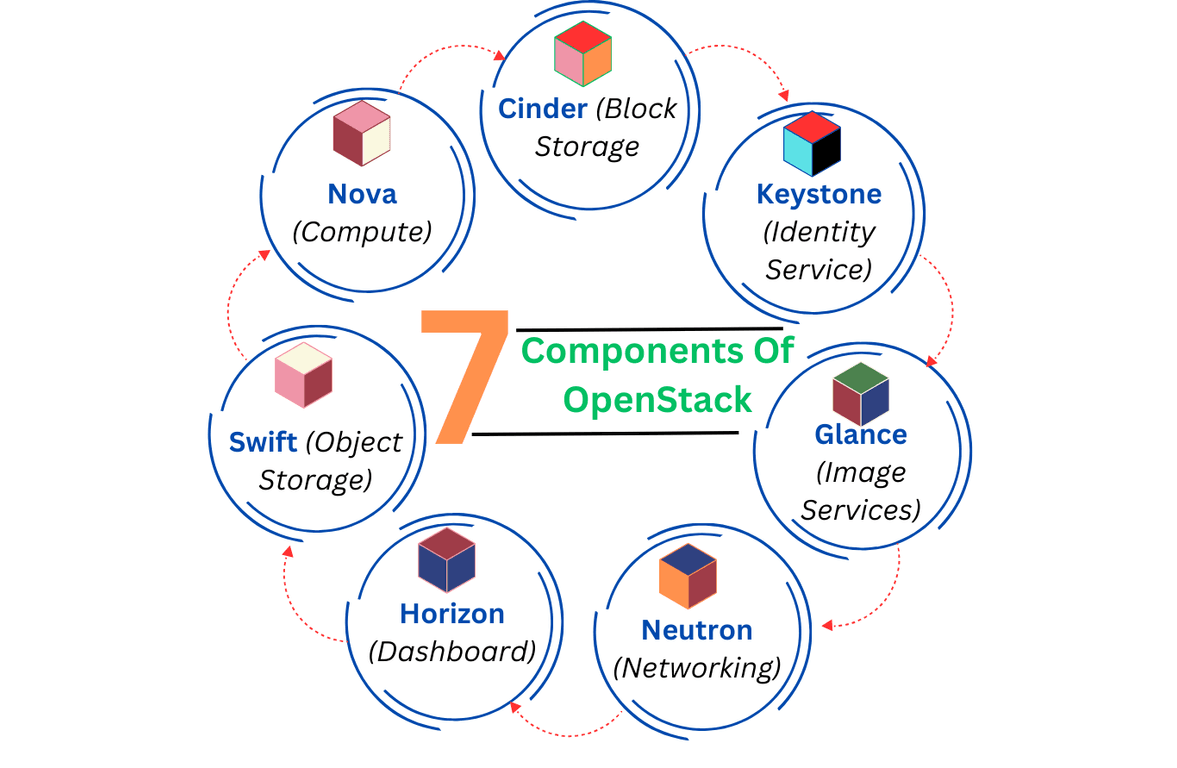
There are several core components of OpenStack cloud architecture. All components play a crucial role in a cloud environment. Here we describe 7 main core components of OpenStack.
1. Nova (Compute)
It manages the networks of virtual machines. This acts as the primary compute engine, and it is responsible for deploying and managing the cloud infrastructure of virtual machines.
2. Swift (Object Storage)
Managing the unstructured data object. It handles the storage and retrieves the data from the object through an API.
6 Differences: Block Storage vs. Object Storage: benefits and uses
3. Cinder (Block Storage)
It works like a hard drive and provides the storage that can be attached to a virtual machine.
6 Differences: Block Storage vs. Object Storage: benefits and uses
4. Neutron (Networking)
It manages the IP address in cloud infrastructure. It provides the connectivity and offers the connectivity between OpenStack and connected devices.
5. Keystone (Identity Service)
As the name suggests, provide high-level authentication and authorization. Provide the user authentication and access control, and it ensures secure access to OpenStack services.
6. Glance (Image Service)
It stores and retrieves virtual machine image files.
7. Horizon (Dashboard)
It provides the user with access to OpenStack on a web browser. It allows administrator access, like a graphical user interface, and simplifies cloud operations.
Uses of OpenStack architecture in cloud environment
Private Clouds
Private clouds provide more substantial benefits for OpenStack. IDC provides the value of the Red Hat OpenStack Platform for private clouds, which is an annual charge for the organizations.
Network functions environment
OpenStack for Network Function Virtualization (NFV) that involves separate network key functions.
Public Clouds
OpenStack leads to building public cloud environments in open source. Organizations publicly trade startups so they can use the OpenStack setup for public clouds with services.
What is an example of a public cloud? Definition, 5 types, and advantages
Containers
OpenStack is suitable for public and private clouds. Containers help to speed up the delivery of application deployment and management.
Know more about cloud computing-related topics
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing: 10 Steps to Implementation Success
- Top 10 best examples of Hybrid cloud computing
- Top 3 Cloud computing solutions: Best definition and benefits
- Cloud Computing Reference Models: Explanation and Example with Diagrams
- 7 Big differences between edge computing and cloud computing: Advantages and disadvantages
- Top 9 Cloud Computing Platforms to know in 2024 and Advantages
- 10 Powerful Cloud Computing Applications: All you need to know
- What is cloud deployment models? Definition, types, comparisons and examples
OpenStack Cloud Architecture Planes
This is divided into two main planes
Control Plane
The control plane is responsible for the management of cloud resources. Keystones, Horizon, APIs, and other core services are the components of the control plane. It manages the security, like authentication and authorization services, and coordination of user services and schedules the resources.
Data Plane
It handles the user data and workloads. Compute instances, which are managed by the Nova component of the data plane. Storage components (Swift and Cinder) and networking components are managed by the neutron in the data plane. Real-time data processing and storage is ensuring that applications and services perform in the data plane.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OpenStack Cloud Architecture
Advantages of OpenStack
- It boosts the resources and scaling up and down that are becoming easy to use.
- The user can deploy the components on OpenStack easily, which is not taking a large amount of time.
- OpenStack resources are more scalable and can be used wisely and efficiently.
Disadvantages of OpenStack
- It is not robust during orchestration and is considered.
- Every API is not compatible and supported by OpenStack with many hybrid cloud environments.
- OpenStack services also become a risk and security breach.
- OpenStack needs the specific hardware requirement that is to limit the types of hardware that can be used. This is the additional investment for OpenStack cloud architecture deployment.
- It has limited vendor support that can make it difficult to get necessary support.
- Upgradation is very typical and time-consuming. It can require additional resources and an expert engineer for smooth work on the new version.
Summary
OpenStack is powerful and flexible for building and managing the cloud architecture. It can be required to add resources and expert people for upgrading for smooth work.
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram