In this article, we will discuss an example of a public cloud and what the advantages and disadvantages of public clouds in cloud computing are. But first of all, let’s discuss the definition of public clouds and their uses.
What is a public cloud?
The public cloud is defined as the availability of computing services by third-party providers. Public clouds make IT resources such as compute, storage, development platforms, and applications available as services over the Internet. Services on the public cloud are available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them. Public clouds are operated by cloud service providers that deliver services over the Internet. Public clouds offer the scalability and flexibility to efficiently meet the collaboration needs of today’s global workforce and deliver significant business value to enterprises. With public clouds, cloud service providers are responsible for managing the systems, allowing businesses to reduce the cost of purchasing, managing, and maintaining on-premises infrastructure. It also offers scalable RAM and flexible bandwidth, allowing businesses to easily grow with their storage needs. In short, public clouds are cost-effective, scalable, accessible from anywhere, and offer automated data backup.
What is public cloud storage?
Public cloud computing is the availability of computing services by third-party providers. Public clouds make IT resources such as compute, storage, development platforms, and applications available as services over the Internet. Public cloud services are available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them.
The public cloud refers to computing services provided over the Internet by third-party providers. Unlike private cloud services, public cloud services are available to anyone who wants to use or purchase them. These services can be free or sold on demand. When sold on demand, users have to pay for the CPU cycles, storage, or bandwidth consumed on a per-use basis.
Public clouds are operated by cloud service providers that deliver services over the Internet. Public clouds provide the scalability and flexibility to efficiently meet the collaboration needs of today’s global workforce and deliver significant business value to enterprises.
Public clouds help businesses save on the cost of purchasing, managing, and maintaining on-premises infrastructure because the cloud service provider is responsible for managing the system. It also offers scalable RAM and flexible bandwidth, allowing businesses to easily expand their storage needs. In short, public clouds are cost-effective, scalable, universally accessible, and offer automated data backups.
Public clouds make IT resources such as compute, storage, development platforms, and applications available as services over the Internet. These services are available on-demand through our self-service portal. With a pay-as-you-go model, public clouds are flexible, scalable, and can be accessed by multiple customers simultaneously. This is called multi-tenancy. Public clouds are usually managed in data centers belonging to service providers. This shared model of public clouds significantly reduces costs for customers.
How Public Cloud Works
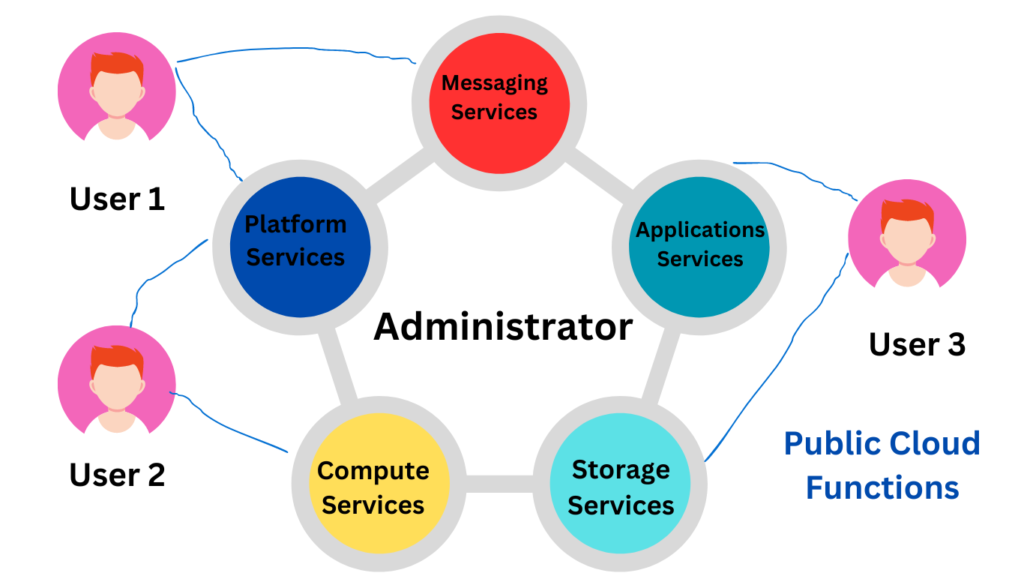
Every public cloud has certain features. These features include:
- Multi-tenant architecture: This means that multiple users (or tenants) leverage shared infrastructure (such as compute resources) to run their workloads. Each tenant’s data is isolated and remains separate from other tenants’ data.
- Scalability: Provides on-demand IT resources on a self-service provisioning basis over the public internet or dedicated networks.
- Flexibility: Public cloud resources are flexible and available on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- High availability: Public cloud hosting providers typically offer a 99.99% SLA uptime guarantee. Data security: customer data is stored with high security on the public cloud. Security features and tools included by cloud providers include DDoS protection, anti-malware protection, and cloud firewalls.
Why the public cloud?
Gone are the days when, if you needed IT resources, you had to configure everything yourself.
Now you can rent the computing power you need, including advanced AI services, developer tools, and GPUs to support virtually any workload.
All are available in the public cloud and are maintained and updated by cloud service providers. You can pay a monthly fee to leverage as many or as few resources as you need.
Public cloud models operate on OPEX, allowing startups to achieve global scale without CAPEX.
Not surprisingly, Gartner predicted that the public cloud services market will grow 17.5% to $213.4 billion in 2019, up from $182.4 billion in 2018.
Gartner forecasts that global public cloud end-user spending will grow by 23% to $332.3 billion in 2021, up from $270 billion in 2020.
Gartner’s latest forecast predicts that global public cloud end-user spending will reach nearly $500 billion in 2022, up from $411 billion in 2021. And by 2023, public cloud end-user spending is expected to reach nearly $600 billion.
Example of a Public Cloud
Amazon Web Services
Amazon Web Services, commonly known as AWS, is a cloud services platform that provides cloud computing infrastructure, database storage, bandwidth, API support, content delivery, and a number of IaaS and PaaS services. Notable AWS services include Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Glacier Storage, Relational Database Service (RDS), Simple Storage Service (S3), Elastic Beanstalk, DynamoDB NoSQL Database, and Elastic Block Store (EBS). We also offer cloud services related to networking, analytics and machine learning, Internet of Things (IoT), mobile services, development, cloud management, cloud security, and more.
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is Microsoft’s public cloud computing platform that provides a wide range of computing, data storage, data analysis, and networking services. Microsoft Azure offers PaaS, SaaS, and IaaS. The cloud platforms support a variety of tools and frameworks (Microsoft and third-party systems) and various programming languages. Azure services can also be used to replace or complement existing on-premises servers.
IBM Cloud
IBM Cloud is IBM’s suite of cloud computing services, offering PaaS and IaaS. The platform is suitable for small teams and organizations as well as large enterprise businesses. IBM Cloud Platform also gives users access to other IBM tools and services, such as IBM Cloud Functions and IBM Watson, as well as third-party services. Developers can use IBM Cloud Platform to build, manage, run, and deploy public clouds locally and on-premises. It supports various programming languages, including Java, PHP, and Python.
Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform (opens in new window) provides a variety of IaaS and PaaS services, including compute, data storage, networking, and developer applications and tools that run on Google hardware. Services offered include Compute Engine, App Engine, Container Engine, Cloud Storage, and BigQuery. Google Cloud Platform services can be accessed by software developers and cloud administrators over a dedicated network connection or over the Internet.
Oracle Cloud
Oracle Cloud is Oracle’s public cloud service that provides servers, storage, networking, applications, and services. We provide PaaS, IaaS, SaaS, and Data as a Service (DaaS). You can use these services to build, run, deploy, integrate, and extend your applications. Oracle Cloud supports various programming languages, tools, databases, and frameworks.
Advantages of Public Cloud
Organizations are moving to the cloud for flexibility and other business benefits.
Here are some of the benefits of the public cloud.
- Cost savings: Moving your organization’s IT operations and workloads to the public cloud can save you a lot of money. Cheaper than a private cloud. Because cloud service providers allow you to make the most of your computing servers, storage, and other hardware,. The multi-tenant architecture ensures that the public cloud infrastructure is used as efficiently as possible.
- Latest technology: cloud solution providers offer their customers the latest technology, including AI/ML technology, serverless computing, and containerized application development.
- Less server management: Your cloud provider manages your servers and network hardware. This eliminates the need for additional IT personnel and ultimately saves money.
- Scalability: Cloud resources are highly scalable and can handle sudden demand or traffic spikes. This makes the public cloud very useful for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) and startups. Start-ups can run a small setup without making large infrastructure investments, which are capital expenditure items with no guaranteed returns or guarantees.
- Flexibility: Customers can access all public cloud services from a single dashboard. For small and medium-sized businesses, including established software development companies, startups, and other enterprises, the flexibility that the public cloud offers is a huge advantage. No one wants a huge infrastructure, and no one wants to be in a situation where their business growth is hampered due to a lack of server resources. You can subscribe to or unsubscribe from different cloud services based on your changing requirements. The monthly cloud service fee varies accordingly. This results in a very manageable OPEX item rather than a huge capital expenditure item.
- Security: Standard public cloud security measures, such as protection against DDoS attacks and anti-malware protection, are an improvement for small and medium-sized businesses from a security perspective.
Related topics about cloud computing: what you should know about?
- Cloud Computing Reference Models: Explanation and Example with Diagrams
- The Ultimate Guide to Cloud Computing: 10 Steps to Implementation Success
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing: 6 Types, Architecture, and Advantages
- 7 Big differences between edge computing and cloud computing: Advantages and disadvantages
- Edge Computing: Definition, Concept, Uses and top 10 best practices cases in 2024
- Cloud Deployment Models: definition, types, comparisons and examples
- Top 9 Cloud Computing Platforms to know in 2024 and Advantages
- 10 Powerful Cloud Computing Applications: All you need to know
- Transforming Technology 2024: Explore the Evolution of Cloud Computing Architecture
follow me : Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, Instagram

1 thought on “What is an example of a public cloud? Definition, 5 types, and advantages”
Comments are closed.